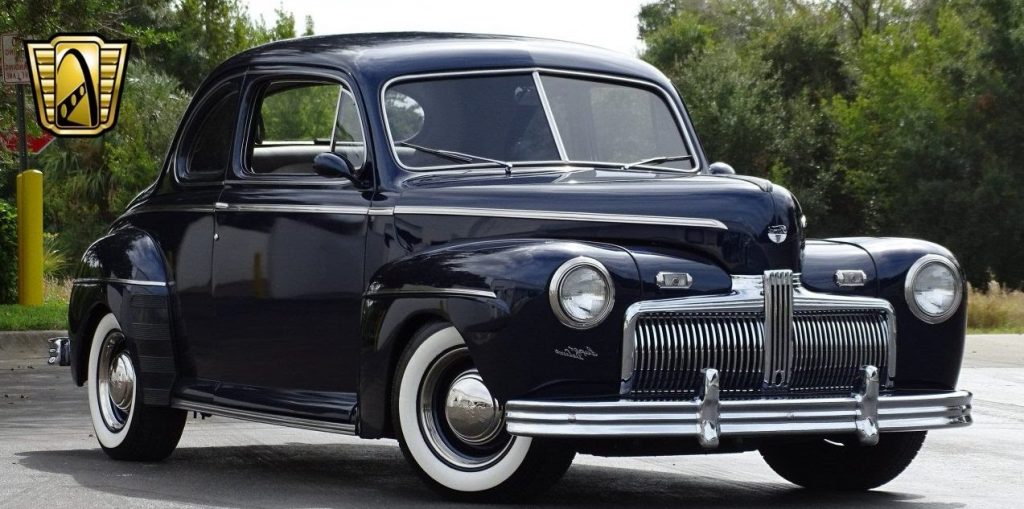
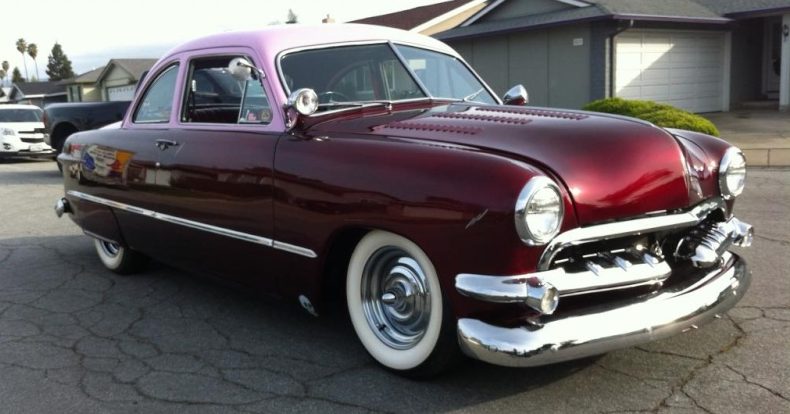
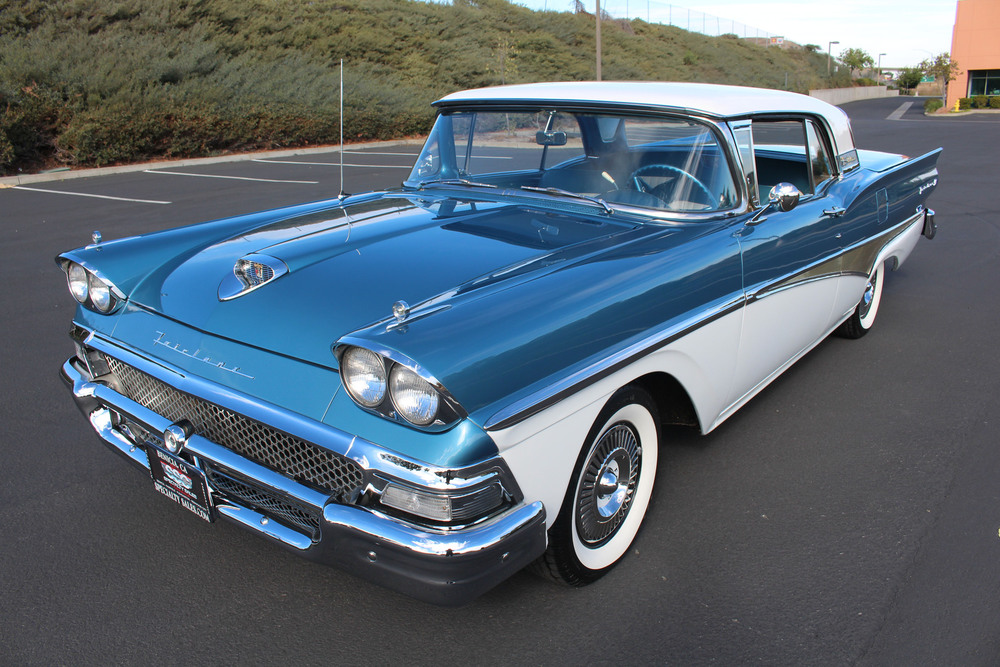
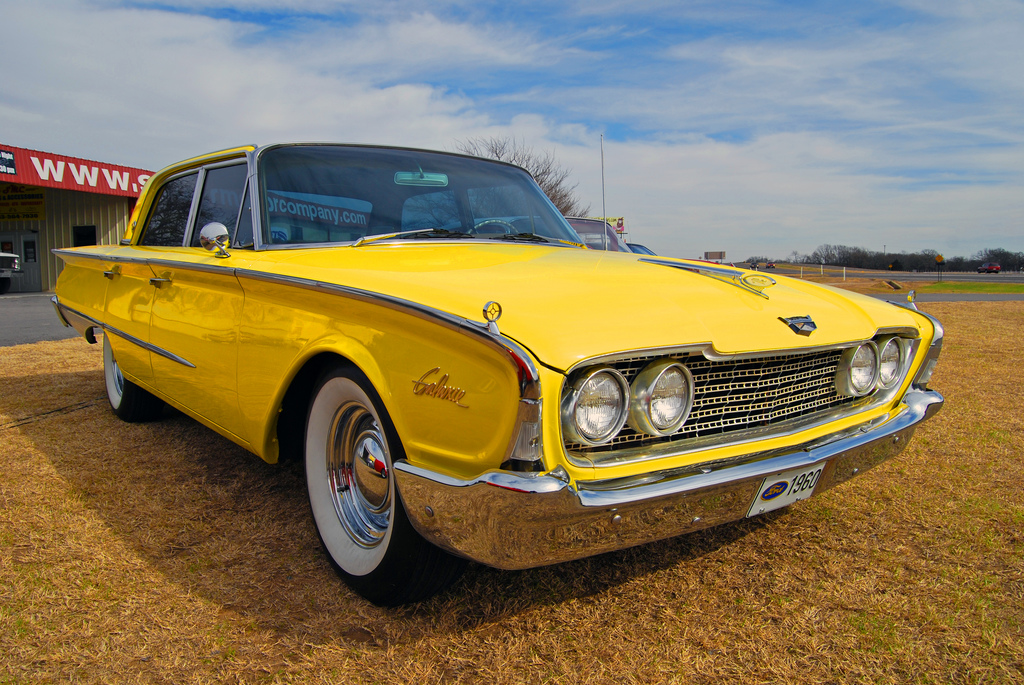
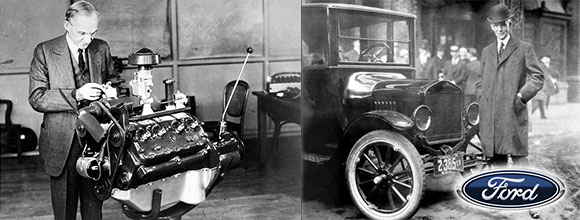
Henry Ford (pictured ca. 1919), founded and led the company, presiding over it during two tenures, 1906–1919 and 1943–1945
The Ford Motor Company is an American automaker, the world’s fifth largest based on worldwide vehicle sales. Based in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit, it was founded by Henry Ford on June 16, 1903. Ford Motor Company would go on to become one of the largest and most profitable companies in the world, as well as being one of the few to survive the Great Depression. The largest family-controlled company in the world, the Ford Motor Company has been in continuous family control for over 110 years. Ford now encompasses two brands: Ford and Lincoln. Ford once owned 5 other luxury brands: Volvo, Land Rover, Jaguar, Aston Martin, and Mercury. Over time, those brands were sold to other companies and Mercury was discontinued.
Foundation[edit]
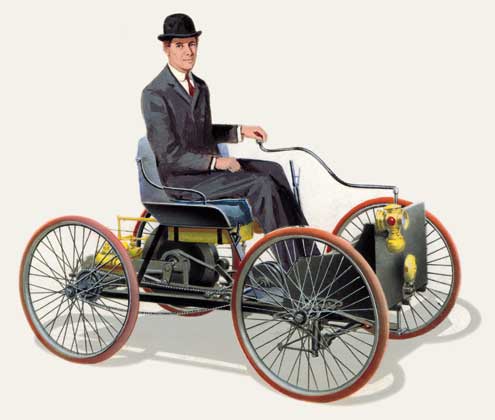
Henry Ford built his first automobile, which he called a quadricycle, at his home in Detroit in 1896. The location has been redeveloped, where the Michigan Building now stands, and the tracks for the Detroit People Mover and the Times Square People Mover station are nearby. At the entrance to the Michigan Building, there is a commemorative plaque identifying the original location of the Ford home. The coal shed has been recreated using the original bricks at Greenfield Village in nearby Dearborn.[1] His initial foray into automobile manufacturing was the Detroit Automobile Company, founded in 1899. The company foundered, and in 1901 was reorganized as the Henry Ford Company. In March 1902, after falling out with his financial backers, Ford left the company with the rights to his name and 900 dollars.[citation needed]
Henry Ford turned to an acquaintance, coal dealer Alexander Y. Malcomson, to help finance another automobile company. Malcomson put up the money to start the partnership «Ford and Malcomson» and the pair designed a car and began ordering parts. However, by February 1903, Ford and Malcomson had gone through more money than expected, and the manufacturing firm of John and Horace Dodge, who had made parts for Ford and Malcomson, was demanding payment.[2] Malcomson, constrained by his coal business demands, turned to his uncle John S. Gray, the president of the German-American Savings Bank and a good friend. Malcomson proposed incorporating Ford and Malcomson to bring in new investors, and wanted Gray to join the company, thinking that Gray’s name would attract other investors. Gray was not interested at first, but Malcomson promised he could withdraw his share at any time, so Gray reluctantly agreed. On the strength of Gray’s name, Malcomson recruited other business acquaintances to invest, including local merchants Albert Strelow and Vernon Fry, lawyers John Anderson and Horace Rackham, Charles T. Bennett of the Daisy Air Rifle Company, and his own clerk James Couzens.[2] Malcomson also convinced the Dodges to accept stock in lieu of payment.[citation needed]
On June 16, 1903, the Ford Motor Company was incorporated, with 12 investors owning a total of 1000 shares. Ford and Malcomson together retained 51% of the new company in exchange for their earlier investments. When the total stock ownership was tabulated, shares in the company were: Henry Ford (255 shares), Alexander Y. Malcomson (255 shares), John S. Gray (105 shares), John W. Anderson (50 shares), Horace Rackham (50 shares), Horace E. Dodge (50 shares), John F. Dodge (50 shares), Charles T. Bennett (50 shares), Vernon C. Fry (50 shares), Albert Strelow (50 shares), James Couzens (25 shares), and Charles J. Woodall (10 shares).[3]
At the first stockholder meeting on June 18, Gray was elected president, Ford vice-president, and James Couzens secretary.[2] Despite Gray’s misgivings, the Ford Motor Company was immediately profitable, with profits by October 1, 1903, of almost $37,000. A dividend of 10% was paid that October, an additional dividend of 20% at the beginning of 1904, and another 68% in June 1904. Two dividends of 100% each in June and July 1905 brought the total investor profits to nearly 300% in just over two years; 1905 total profits were almost $300,000.[2]
However, there were internal frictions in the company that Gray was nominally in charge of. Most of the investors, both Malcomson and Gray included, had their own businesses to attend to; only Ford and Couzens worked full-time at the company. The issue came to a head when the principal stockholders, Ford and Malcomson, quarreled over the future direction of the company. Gray sided with Ford. By early 1906 Malcomson was effectively frozen out of the Ford Motor Company, and in May sold his shares to Henry Ford.[2] John S. Gray died unexpectedly in 1906, and his position as Ford’s president was taken over by Ford himself soon afterward.[2]
Ford was subject to lawsuits or threats from the Association of Licensed Automobile Manufacturers early in its history. The association claimed patent rights to most gasoline-powered automobiles. After several years of legal wrangling, the association eventually dropped its case against Ford in 1911.[citation needed]
Early developments and assembly line[edit]
The coal shed on Bagley Street, Detroit where Henry Ford built his first car in 1896.
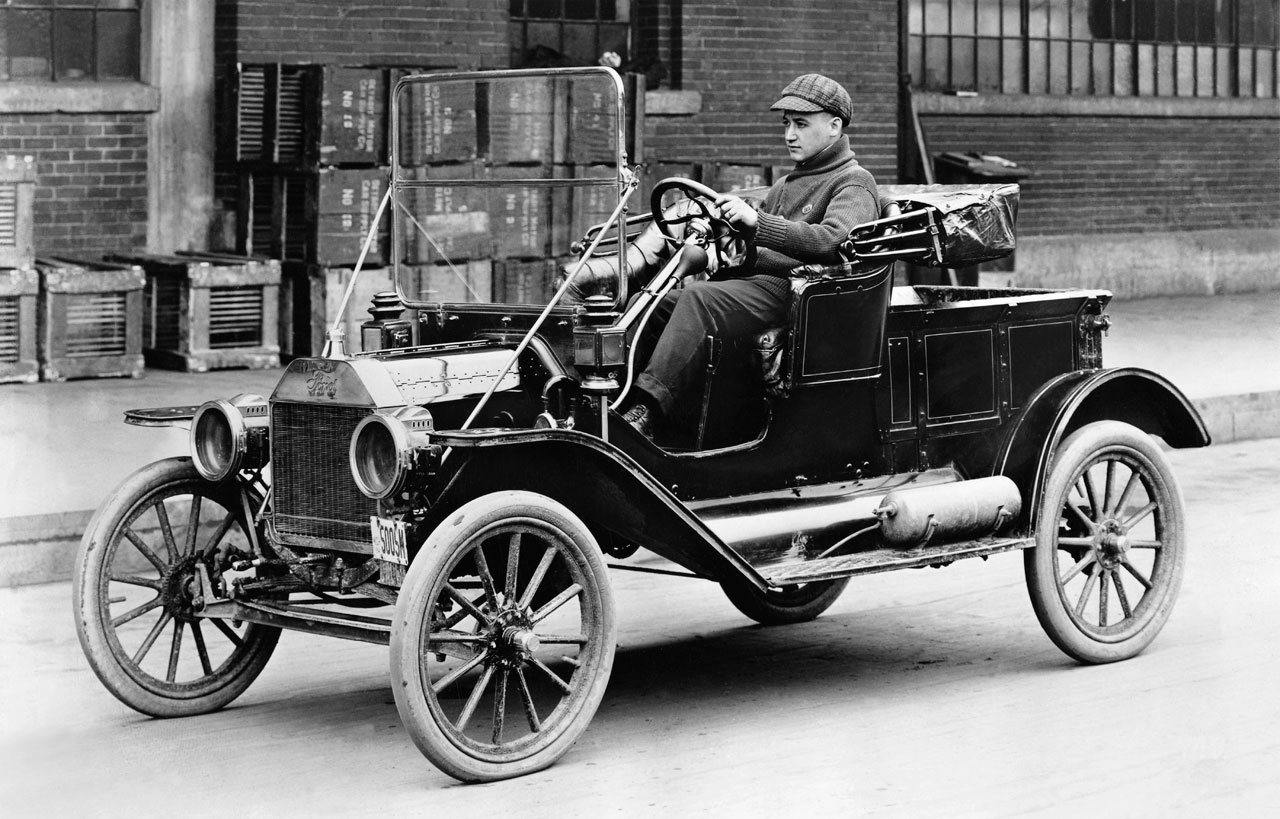
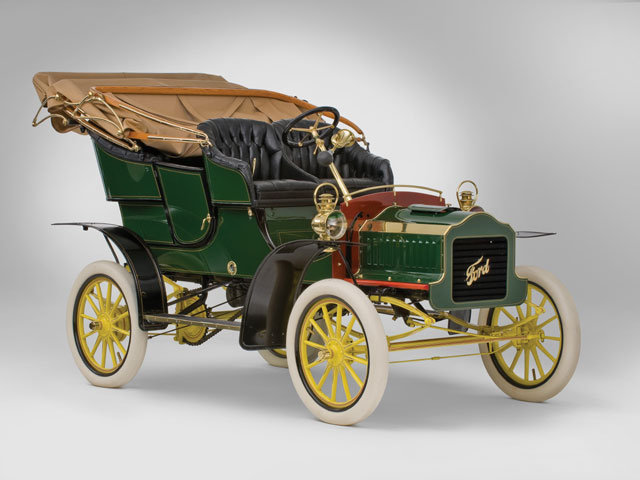
During its early years, the company produced a range of vehicles designated, chronologically, from the Ford Model A (1903) to the Model K and Model S (Ford’s last right-hand steering model)[4] of 1907.[4] The K, Ford’s first six-cylinder model, was known as «the gentleman’s roadster» and «the silent cyclone», and sold for US$2800;[4] by contrast, around that time, the Enger 40 was priced at US$2000,[5] the Colt Runabout US$1500,[6] the high-volume Oldsmobile Runabout[7] US$650, Western’s Gale Model A US$500,[8] and the Success hit the amazingly low US$250.[7]
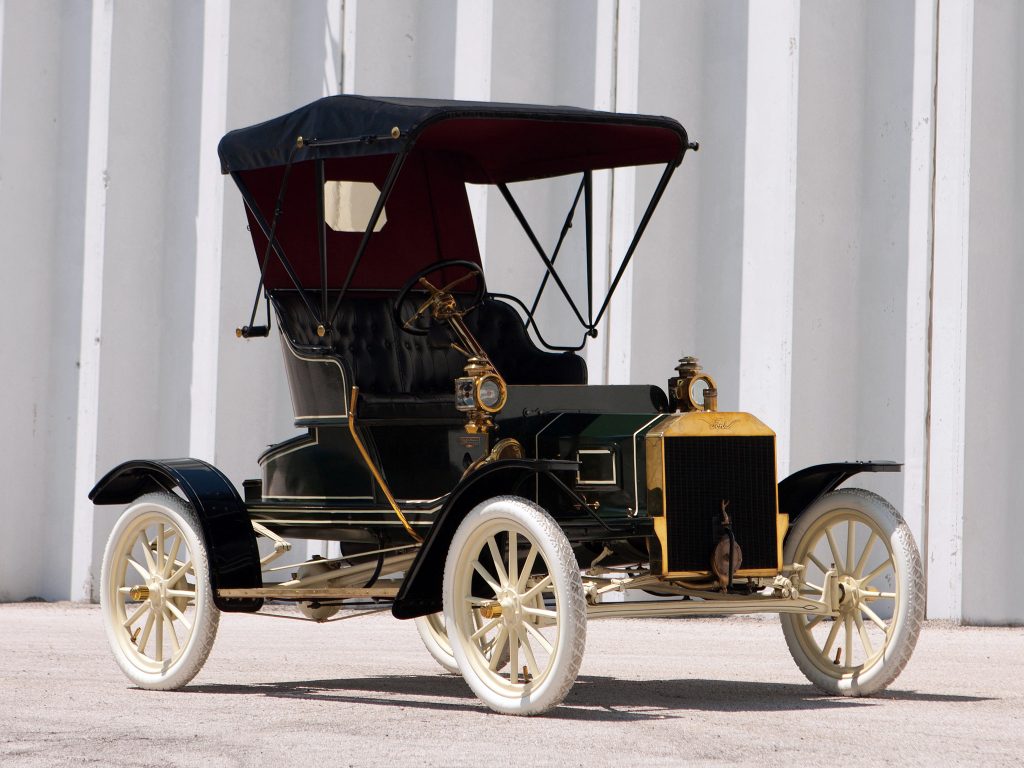
In 1908, Henry Ford introduced the Model T. Earlier models were produced at a rate of only a few a day at a rented factory on Mack Avenue in Detroit, Michigan and later at the Piquette Avenue Plant (the first company-owned factory), with groups of two or three men working on each car from components made to order by other companies (what would come to be called an «assembled car»). The first Model Ts were built at the Piquette Avenue Plant and in the car’s first full year of production, 1909, just over 10,000 Model Ts were built. As demand for the car grew, the company moved production to the much larger Highland Park Plant in 1910. In 1911, 69,762[9] Model Ts were produced, with 170,211 in 1912.[9] By 1913, the company had developed all of the basic techniques of the assembly line and mass production. Ford introduced the world’s first moving assembly line that year, which reduced chassis assembly time from 12+1⁄2 hours in October to 2 hours 40 minutes (and ultimately 1 hour 33 minutes),[9] and boosted annual output to 202,667 units that year[9] After a Ford ad promised profit-sharing if sales hit 300,000 between August 1914 and August 1915,[10] sales in 1914 reached 308,162, and 501,462 in 1915;[9] by 1920, production would exceed one million a year.
These innovations were hard on employees, and turnover of workers was very high, while increased productivity reduced labor demand.[9] Turnover meant delays and extra costs of training, and use of slow workers. In January 1914, Ford solved the employee turnover problem by doubling pay to $5 a day[11] cutting shifts from nine hours to an eight-hour day for a 5-day work week (which also increased sales; a line worker could buy a T with less than four months’ pay),[9] and instituting hiring practices that identified the best workers, including disabled people considered unemployable by other firms.[9] Employee turnover plunged, productivity soared, and with it, the cost per vehicle plummeted. Ford cut prices again and again and invented the system of franchised dealers who were loyal to his brand name. Wall Street had criticized Ford’s generous labor practices when he began paying workers enough to buy the products they made.[12]
Ford assembly line (1913)
While Ford attained international status in 1904 with the founding of Ford of Canada, it was in 1911 the company began to rapidly expand overseas, with the opening of assembly plants in Ireland (1917), England and France, followed by Denmark (1923), Germany (1925), Austria (1925),[9] and Argentina (1925).[13] A factory was opened in Japan (1925) at Yokohama, and also in South Africa (1924)[14] and Australia (1925) as subsidiaries of Ford of Canada due to preferential tariff rules for Commonwealth countries. By the end of 1919, Ford was producing 50 percent of all cars in the United States, and 40% of all British ones;[9] by 1920, half of all cars in the U.S. were Model Ts. (The low price also killed the cyclecar in the U.S.)[9] The assembly line transformed the industry; soon, companies without it risked bankruptcy. Of 200 U.S. car makers in 1920, only 17 were left in 1940.[9]
It also transformed technology. Henry Ford is reported to have said, «Any customer can have a car painted any color that he wants so long as it is black.» Before the assembly line, Ts had been available in a variety of colors, including red, blue, and green, but not black. Now, paint had become a production bottleneck; only Japan Black dried quickly enough, and not until Duco lacquer appeared in 1926 would other colors reappear on the T.[9]
In 1915, Henry Ford went on a peace mission to Europe aboard a ship, joining other pacifists in efforts to stop World War I. This led to an increase in his personal popularity. Ford would subsequently go on to support the war effort with the Model T becoming the underpinnings for Allied military vehicles, like the Ford 3-Ton M1918 tank, and the 1916 ambulance.[citation needed]
Post-World War I developments[edit]
Ford 1916 Model T Field Ambulance. This canvas on wood frame model was used extensively by the British & French as well as the American Expeditionary Force in World War I. Its top speed was 45 mph (72 km/h), produced by a 4-cylinder water-cooled engine
By 1916, the company had accumulated a capital surplus of $60 million, but Henry Ford declared that he intended to end special dividends for shareholders in favor of massive investments in new plants, including the River Rouge plant, allowing Ford to dramatically increase production, and the number of people employed at his plants, at the same time as cutting the prices of his cars. The Dodge brothers, John Francis Dodge and Horace Elgin Dodge, the largest non-family shareholders, with 10% of the company, objected and took Ford to court in 1917 in an often cited case, Dodge v. Ford Motor Company.[15] The judge found in their favor requiring a $19million special dividend. The decision was then upheld in the 1919 appeal to the Michigan Supreme Court which stated that:[citation needed]
A business corporation is organized and carried on primarily for the profit of the stockholders. The powers of the directors are to be employed for that end. The discretion of directors is to be exercised in the choice of means to attain that end, and does not extend to a change in the end itself, to the reduction of profits, or to the non-distribution of profits among stockholders in order to devote them to other purposes …
In response Henry Ford determined to buy out the remaining shareholders. To encourage this, he threatened to leave and set up a rival company, offering to buy out the minority shareholders, at varying prices. He gained complete control in July 1919 at a cost of $125 million, made up of $106 million of the stock and $19 million in court-ordered dividend, financed with a $75 million loan from two eastern banks. The Dodge brothers received $25 million.[16] At this time Edsel Ford also succeeded his father as president of the company, although Henry still kept a hand in management.[citation needed]
While prices were kept low through highly efficient engineering, the company used an old-fashioned personalized management system, and neglected consumer demand for improved vehicles. So, while four-wheel brakes were invented by Arrol-Johnson (and were used on the 1909 Argyll),[9] they did not appear on a Ford until 1927,[9] only a year before Chevrolet. Ford steadily lost market share to GM and Chrysler, as these and other domestic and foreign competitors began offering fresher automobiles with more innovative features and luxury options. GM had a range of models from relatively cheap to luxury, tapping all price points in the spectrum, while less wealthy people purchased used Model Ts. The competitors also opened up new markets by extending credit for purchases, so consumers could buy these expensive automobiles with monthly payments. Ford initially resisted this approach, insisting such debts would ultimately hurt the consumer and the general economy. Ford eventually relented and started offering the same terms in December 1927, when Ford unveiled the redesigned Model A, and retired the Model T after producing 15 million units. An early version of the Ford script in the oval badge was first used on the 1928 Model A; the Ford script had been created in 1903 by Childe Harold Wills, and the oval trademark in 1907.[17]
Lincoln Motor Company[edit]
On February 4, 1922, Ford expanded its reach into the luxury auto market through its acquisition of the Lincoln Motor Company from Henry M. Leland who had founded and named the company in 1917 for Abraham Lincoln whom Henry Leland admired. The Mercury division was established later in 1938 to serve the mid-price auto market between the Ford and Lincoln brands.[18]
Ford Motor Company dedicated the largest museum of American History in 1929, The Henry Ford. Henry Ford would go on to acquire Abraham Lincoln’s chair, which he was assassinated in, from the owners of Ford’s Theatre. Abraham Lincoln’s chair would be displayed along with John F. Kennedy’s Lincoln presidential limousine in the Henry Ford Museum & Greenfield Village in Dearborn, known today as The Henry Ford. Kennedy’s limousine was leased to the White House by Ford.
Fordlândia[edit]
In 1928, Henry Ford negotiated a deal with the government of Brazil for a plot of land in the Amazon Rainforest. There, Ford attempted to cultivate rubber for use in the company’s automobiles. After considerable labor unrest, social experimentation, and a failure to produce rubber, and after the invention of synthetic rubber, the settlement was sold in 1945 and abandoned.[19]
The Great Depression[edit]
During the Great Depression, Ford in common with other manufacturers, responded to the collapse in motor sales by reducing the scale of their operations and laying off workers. By 1932, the unemployment rate in Detroit had risen to 30%[20] with thousands of families facing real hardship. Although Ford did assist a small number of distressed families with loans and parcels of land to work, the majority of the thousands of unskilled workers who were laid off were left to cope on their own. However, Henry Ford angered many by making public statements that the unemployed should do more to find work for themselves.[citation needed]
This led to Detroit’s Unemployed Council organizing the Ford Hunger March. On March 7, 1932, some 3,000–5,000 unemployed workers assembled in West Detroit to march on Ford’s River Rouge plant to deliver a petition demanding more support. As the march moved up Miller Road and approached Gate 3 the protest turned ugly. The police fired tear gas into the crowd and fire trucks were used to soak the protesters with icy water. When the protesters responded by throwing rocks, the violence escalated rapidly and culminated in the police and plant security guards firing live rounds through the gates of the plant at the unarmed protesters. Four men were killed outright and a fifth died later in the hospital. Up to 60 more were seriously injured.[21]
Soviet Fords and the Gorki[edit]
In May 1929 the Soviet Union signed an agreement with the Ford Motor Company. Under its terms, the Soviets agreed to purchase $13 million worth of automobiles and parts, while Ford agreed to give technical assistance until 1938 to construct an integrated automobile-manufacturing plant at Nizhny Novgorod. Many American engineers and skilled auto workers moved to the Soviet Union to work on the plant and its production lines, which was named Gorkovsky Avtomobilny Zavod (GAZ), or Gorki Automotive Plant in 1932. A few American workers stayed on after the plant’s completion, and eventually became victims of Stalin’s Great Terror, either shot[22] or exiled to Soviet gulags.[23] In 1933, the Soviets completed construction on a production line for the Ford Model-A passenger car, called the GAZ-A, and a light truck, the GAZ-AA. Both these Ford models were immediately adopted for military use. By the late 1930s production at Gorki was 80,000-90,000 «Russian Ford» vehicles per year. With its original Ford-designed vehicles supplemented by imports and domestic copies of imported equipment, the Gorki operations eventually produced a range of automobiles, trucks, and military vehicles.[citation needed]
Era of neutrality[edit]
An advertisement for «The £100 Ford saloon», 1936
During the first 27 months of World War II, when the U.S. was neutral (to December 1941), Ford was hesitant to participate in the Allied military effort. Ford insisted that peaceful trade was the best way to avoid war. Ford had a subsidiary in Germany. In 1936, a Ford executive visiting Germany was informed by a Nazi official that Ford’s Cologne plant manager was a Jew (he had one grandparent who was Jewish), prompting discussions at Ford offices in both Germany and the U.S. Heinrich Albert, Ford’s Germany-U.S. liaison, insisted that the manager be fired. The manager was replaced by Robert Schmidt, who would play an important role in Germany’s war effort.[24]
Henry Ford had said war was a waste of time, and did not want to profit from it.[12][25] He was concerned the Nazis during the 1930s might nationalize Ford factories in Germany. Ford nevertheless established a close collaboration with Germany’s Nazi government before the war—so close, in fact, that Ford received, in July 1938, the Grand Cross of the German Eagle medal from the regime.[24] Ford’s outspoken anti-semitism, including his newspaper, The Dearborn Independent, which published The Protocols of the Elders of Zion, also lent credence to the view that he sympathized with the Nazis.[24][26] In the spring of 1939, the Nazi government assumed day-to-day control of many foreign-owned factories in Germany. However, Ford’s Dearborn headquarters continued to maintain a 52% ownership over its German factories but with no voice or control or financial reward. Ford factories contributed significantly to the buildup of Germany’s armed forces. Ford negotiated a resource-sharing agreement that allowed the German military to access scarce supplies, particularly rubber. During this same period, Ford was hesitant to participate in the Allied military effort.[24] In June 1940, after France had fallen to the Wehrmacht, Henry Ford personally vetoed a plan to build airplane engines for the Allies.[27]
Wartime[edit]
The company enthusiastically supported the war effort after Pearl Harbor, making it a major component of the «Arsenal of Democracy» that President Roosevelt had promised would mobilize industrial resources to win the war. Henry, aged 76 and early senile, played a minor role even though he had 55% ownership of the company stock. His son Edsel Ford, the company president and owner of 42% of the stock, had never been a pacifist like his father and now made all the decisions.[28]
The company produced 390,000 tanks and trucks, 27,000 engines, 270,000 Jeeps, over 8,000 B-24 Liberators, and hundreds of thousands of parts, gun mounts, and machine tools for the war effort.[29] It ranked third among corporations in the value of wartime production contracts.[30]
The company’s new Willow Run factory was designed for the production of B-24 bombers although the production line was initially characterized by bungling and incompetence.[24] Ford’s efforts benefited the Allies as well as the Axis. After Bantam invented the Jeep, the US War Department handed production over to Ford and Willys.[31][32]
The U.S. Treasury Department investigated Ford for alleged collaboration with German-run Ford plants in occupied France, but did not find conclusive evidence. By 1998, Ford’s business dealings with Nazi Germany and alleged profiteering from Nazi Germany became the subject of lawsuits.[27] After the war, Schmidt and other Nazi-era managers kept their jobs with Ford’s German division.[27] In the United Kingdom, Ford built a new factory in Trafford Park, Manchester during WWII where over 34,000 Rolls-Royce Merlin aero engines were completed by a workforce trained from scratch.[33][34]
Post-World War II developments[edit]
|
|
This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (May 2013) |
In 1943, a despondent Edsel Ford died of stomach cancer. Henry decided then to resume direct control of the company, but this proved a very poor idea as he was 78 years old and suffering from heart problems and atherosclerosis. His mental state was also questionable, and there was a very real possibility that the company would collapse if he died or became incapacitated. The Roosevelt Administration had a contingency plan in place to nationalize Ford if need be so that they wouldn’t lose vital military production.[citation needed]
At this point, Ford’s wife and daughter-in-law intervened and demanded that he turn control over to his grandson[35] Henry Ford II. They threatened to sell off their stock (amounting to half the company’s total shares) if he refused. Henry was infuriated, but there was nothing he could do, and so he gave in. When Henry II, who came to be called affectionately «Hank the Deuce,» assumed command, the company was losing US$9 million a month and in financial chaos.[35]
Henry Ford died of a brain hemorrhage on April 7, 1947. Mourners passed by at a rate of 5,000 each hour at the public viewing on Wednesday of that week at Greenfield Village in Dearborn. The funeral service for Henry Ford was held at the Cathedral Church of St. Paul in Detroit on Thursday April 9, 1947.[36] At the funeral service, 20,000 people stood outside St. Paul’s Cathedral in the rain with 600 inside,[36] while the funeral had attracted national attention as an estimated seven million people had mourned his death (according to A&E Biography).
Ernest R. Breech, head of Bendix Aviation,[35] was hired in 1946, and became first executive vice president, then board chairman in 1955. Henry II served as president from 1945 to 1960, and as chairman and CEO from 1960 to 1980. In 1956, Ford became a publicly traded corporation. The Ford family maintains about 40% controlling interest in the company, through a series of Special Class B preferred stocks. Also in 1956, following its emphasis on safety improvements in new models, Motor Trend awarded the company its «Car of the Year» award.[37]
In 1946, Robert McNamara joined Ford as manager of planning and financial analysis. He advanced rapidly through a series of top-level management positions to the presidency of Ford on 9 November 1960, one day after John F. Kennedy’s election. The first company head selected outside the Ford family, McNamara had gained the favor of Henry Ford II, and had aided in Ford’s expansion and success in the postwar period. Less than five weeks after becoming president at Ford, he accepted Kennedy’s invitation to join his cabinet, as Secretary of Defense.[citation needed]
Ford introduced the iconic Thunderbird in 1955 and the Edsel brand automobile line in 1958, following a US$250 million research and marketing campaign, which had failed to ask questions crucial for the marque’s success.[38] The Edsel was cancelled after less than 27 months in the marketplace in November 1960. The corporation bounced back from the failure of the Edsel by introducing its compact Falcon in 1960 and the Mustang in 1964. By 1967, Ford of Europe was established.[citation needed]
Lee Iacocca was involved with the design of several successful Ford automobiles, most notably the Mustang. He was also the «moving force,» as one court put it, behind the notorious Pinto. He promoted other ideas which did not reach the marketplace as Ford products. Eventually, he became the president of the company, but clashed with «Bunkie» Knudsen as well as Henry II and ultimately, on July 13, 1978, he was fired by Henry Ford II, despite the company’s having earned a $2.2 billion profit for the year. Chrysler soon hired Iacocca, which he returned to profitability during the 1980s.[citation needed]
In 1966, Ford hired famous designer Paul Rand to refresh its logo. Nevertheless, Rand’s proposal (image) was finally dismissed by Henry Ford II.[39]
In 1942, Elsa Iwanowa, who was then 16 years old and a resident of Rostov in the Soviet Union, and many other citizens of countries that were occupied by the Wehrmacht were transported in cattle cars to the western part of Germany, where they were displayed to visiting businessmen. From there Iwanowa and others were forced to become slave laborers for Ford’s German subsidiary, which had become separated from the Dearborn headquarters as a result of the U.S. declaration of war. «On March 4, 1998, fifty-three years after she was liberated from the German Ford plant, Elsa Iwanowa demanded justice, filing a class-action lawsuit in U.S. District Court against the Ford Motor Company.»[40] In court, Ford admitted that Iwanowa and many others like her were «forced to endure a sad and terrible experience»; Ford, however, moved to have the suit dismissed on the grounds that it would be best redressed on «a nation-to-nation, government-to-government» basis.[24] In 1999, the court dismissed Iwanowa’s suit. At about the same time, a number of German companies, including GM subsidiary Opel, agreed to contribute $5.1 billion to a fund to compensate the surviving slave laborers.[24] After being the subject of much adverse publicity, Ford, in March 2000, agreed to contribute $13 million to the compensation fund.[citation needed]
In 1979 Philip Caldwell became chairman, succeeded in 1985 by Donald Petersen. Harold Poling served as chairman and CEO from 1990 to 1993. Alex Trotman was chairman and CEO from 1993 to 1998, and Jacques Nasser served at the helm from 1999 to 2001. Henry Ford’s great-grandson, William Clay Ford Jr., is the company’s current chairman of the board and was CEO until September 5, 2006, when he named Alan Mulally from Boeing as his successor.[citation needed]
Recapitalization, restructuring[edit]
Cash hoarding[edit]
In April 2000 the Ford Motor Company announced its recapitalization plan distributing about half of its $24 billion cash hoard, and paying a $10 billion special dividend, and the issuance of additional stock to the Ford family, to provide more flexibility for the Ford family in terms of estate planning. In 2000 Ford’s cash hoard was the largest of any company in the world.[41]
As of 2006, the Ford family owned about 5% of company shares outstanding.[42]
In December 2006, Ford announced it would mortgage all assets, including factories and equipment, office property, intellectual property (patents and blue oval trademarks), and its stakes in subsidiaries, to raise $23.4 billion in cash. The secured credit line is expected to finance product development during the restructuring through 2009, as the company expects to burn through $17 billion in cash before turning a profit. The action was unprecedented in the company’s 103-year history.[43][44]
At the end of 2012 Ford Motor Company’s cash balance was $22.9 billion and was listed as ten on the list of U.S. non-financial corporation sector’s top ten cash kings by Moody’s Investors Service in their March 2013 annual report on Global Credit Research.[45][46][47]
General corporate timeline[edit]
Henry Ford and the Quadricycle
- 1896: Henry Ford builds his first vehicle – the Quadricycle – on a buggy frame with 4 bicycle wheels.
- 1898: Ford creates the Detroit Automobile Company; two and a half years later it is dissolved.
- 1901: Ford wins high-profile car race in Grosse Pointe, Michigan. The Henry Ford Company is incorporated but discontinued the following year only to be reinvigorated by Henry Leland as the Cadillac Motor Company.
- 1903: Ford Motor Company incorporated with 11 original investors. The Model A «Fordmobile» is introduced – 1,708 cars are produced.
- 1904: Ford Motor Company of Canada incorporated in Walkerville, Ontario. Henry Ford teams up with Harvey Firestone of Firestone Tires
- 1906: Ford becomes the top selling brand in the US, with 8,729 cars produced.
- 1908: Model T is introduced. 15 million are produced through 1927.
- 1909: Ford Motor Company (England) established, otherwise referred to as Ford of Britain
- 1911: Ford opens first factory outside North America – in Manchester, England.
- 1913: The moving assembly line is introduced at Highland Park assembly plant, making Model T production 8 times faster. Ford opens second world branch in Argentina as Ford Motor Argentina.
- 1914: Ford introduces $5 ($135, adjusted for inflation) wage for a workday – double the existing rate.
- 1916: Société française des automobiles Ford incorporated in Bordeaux, France, by Percival Perry, the head of Ford of Britain.
- 1918: Construction of the Rouge assembly complex begins.
- 1919: Edsel Ford succeeds Henry as Company President.
- 1920: Ford temporarily shuts down due to low sales. After removing unnecessary administrative expenses and waste, Ford reopens.[48]
- 1921: Ford production exceeds 1 million cars per year, nearly 10 times more than Chevrolet – the next biggest selling brand.
- 1922: Ford purchases Lincoln Motor Company for US$8 million ($130 million, adjusted for inflation).
- 1925: Ford introduces Ford Tri-Motor airplane for airline services, and a factory was built in Yokohama, Japan in February.
- 1926: Ford Australia is founded in Geelong, Victoria, Australia,
- 1927: Model T production ends, Ford introduces the next generation Model A, from the Rouge complex.
- 1929: Ford regains production crown, with annual production peaking at 1.5 million cars
- 1931: Ford and Chevy brands begin to alternate as U.S. production leaders, in battle for automobile sales during the Great Depression.
- 1932: Ford introduces the one-piece cast V8 block. It makes the Model 18 the first low-priced V8-powered car. In London Royal Albert Hall the Model 19, or as it was marketed Model Y, are introduced February 19. The first of a long line of small European Fords.[49]
- 1936: Lincoln-Zephyr is introduced.
- 1938: The German consul at Cleveland awards Henry Ford the Grand Cross of the German Eagle, the highest medal Nazi Germany could bestow on a foreigner. There is some evidence Ford had Nazi sympathies, at least before World War II. He may have financed some Nazi activities, and was active in anti-semitic efforts.
- 1939: Mercury division is formed to fill the gap between economical Fords and luxury Lincolns. Operated as a division at Ford until 1945
- 1941: The Lincoln Continental is introduced. Ford begins building general-purpose «jeep» for the military. First labor agreement with UAW-CIO covers North American employees.
- 1942: Production of civilian vehicles halted, diverting factory capacity to producing B-24 Liberator bombers, tanks, and other products for the war effort.
- 1943: Edsel Ford dies of cancer at the age of 49, Henry Ford resumes presidency.
- 1945: Henry Ford II becomes president.
- 1945: Lincoln and Mercury are combined into a single division.
- 1946: Ford sues the Allies for damages done to his factories in Dresden during the infamous bombing, and wins compensation.[citation needed]
- 1946: The Whiz Kids, former US Army Air Force officers, are hired to revitalize the company. Automobile production resumes.
- 1947: Henry Ford dies of cerebral hemorrhage at the age of 83; Henry Ford II becomes new chairman.
- 1948: F-1 Truck introduced. Lincoln Continental is introduced.
- 1949: The ’49 Ford introduces all-new post-war era cars. The «Woody» station wagon is introduced.
- 1953 Ford Canada Headquarters and Car Plant opens in Oakville, Ontario
- 1953: The company celebrated its 50th anniversary by purchasing two hours of prime time on the CBS and NBC networks for The Ford 50th Anniversary Show that attracted an audience of 60 million.[50]
- 1954: Thunderbird introduced as a personal luxury car with a V8. Ford begins crash testing, and opens Arizona Proving Grounds.
- 1956: Ford World Headquarters dedicated, September 26, 1956
- 1956: $10,000 ($100,905, adjusted for inflation) Lincoln Continental Mark II introduced. Ford goes public with common stock shares. Ford’s emphasis on safety with its Lifeguard option package, including seat belts and dash padding, earns the company Motor Trend‘s «Car of the Year» award.[37]
- 1957: Ford launches the Edsel brand of automobiles in the fall of 1957 as 1958 models. Ford is top selling brand, with 1.68 million automobiles produced.
- 1959: Ford Credit Corporation formed to provide automotive financing.
- 1959: Ford withdraws the 1960 model Edsels from the market in November 1959.
- 1960: Ford Galaxie and compact Ford Falcon introduced.
- 1960: Robert McNamara is appointed president of Ford by Chairman Henry Ford II.
- 1960: Ford President Robert McNamara appointed Secretary of Defense by President elect John F. Kennedy.
- 1962: Ford of Britain launches first generation of the Ford Cortina. It would dominate the mid-size family segment in Europe for the next 20 years.
Mustang Serial #1, the first car launched in 1964
- 1964: Ford Mustang the car that started the «pony car» class, Ford GT40 challenges Ferrari and Porsche at LeMans.
- 1965: Ford brand US sales exceed 2 million units. Ford of Germany and Ford of Britain jointly launch the first generation Ford Transit range of panel vans.
- 1965: Ford Galaxie 500 LTD debuts, advertised as quieter than a Rolls-Royce
- 1966: Ford Bronco sport utility vehicle introduced.
- 1967: Ford of Europe is established by merging the operations of Ford of Britain and Ford of Germany.
- 1967: Ford opens Talbotville car plant in St. Thomas, Ontario
- 1968: Lincoln Mark Series is introduced as the company’s first personal luxury car to compete with the Cadillac Eldorado. Ford of Europe launches first generation Ford Escort.
- 1970: Ford Maverick are introduced. Ford establishes Asia Pacific operations. Ford of Europe launches the third generation Cortina/Taunus – merging the two previously independent product lines under a common platform. Saarlouis assembly plant in Germany opens.
- 1972: Retractable seat belts introduced. «Project Bobcat» – Ford’s largest single vehicle project to date, is initiated to develop the company’s first front-wheel drive compact hatchback model. Will emerge as the Fiesta in 1976.
- 1973: Ford US brand sales reaches an all-time high of 2.35 million vehicles produced.
- 1974: Ford Mustang II debuts as a smaller more economical pony car. Ford of Europe launches second generation Capri – is again sold under the Mercury brand in North American markets.
- 1975: Ford Granada and Mercury Monarch introduced, Production of the Maverick dropped in 1975 with the release of the Granada as a more European-style luxury compact. Ford of Europe launches the second generation Escort.
- 1976: Ford of Europe launches formally launches the first generation Ford Fiesta, and later that year the fourth generation Cortina/Taunus. Opening of the Valencia assembly plant in Spain.
- 1977: Ford of Europe launches the second-generation Granada.
- 1978: Ford Motor Company celebrates 75th anniversary. Continental Mark V and Thunderbird available with «Diamond Jubilee Edition» packages. Fiesta is imported from Europe as an entry into the economy segment.
- 1979: Ford acquires 25% stake in Mazda. Ford becomes the final American automaker to introduce downsized full-size cars with radically smaller Panther platform.
- 1980: Ford of Europe launches the third generation Escort, it is voted European Car of the Year for 1981.
- 1981: The Lincoln Town Car and Ford Escort are introduced. Fiesta discontinued in North America.
- 1982: Ford of Europe introduce the Ford Sierra, ending production of the stalwart Cortina/Taunus after 20 years and four generations.
- 1983: Ford launches a redesigned «aero design» Thunderbird. In a model shift, the Granada is discontinued in North America, replaced by a facelifted model re-branded as the LTD. All full-size models are now LTD Crown Victorias/Country Squires.
- 1984: Ford Tempo and Mercury Topaz are introduced, replacing the Ford Fairmont/Mercury Zephyr.
- 1985: Ford Scorpio launched by Ford of Europe. Replaces Granada as its full-size offering and is voted European Car of the Year for 1986, Ford’s second COTY win in the 1980s. Merkur brand launched to market the Sierra and Scorpio models in North America. Purchases First Nationwide Financial Corporation, a savings and loan, for $493 million in cash.[51] Ford Taurus introduced with dramatic «aero design» styling, along with Ford Aerostar minivan. Taurus is one of Ford’s best-selling models, with 7,000,000 units sold ranks among the 4th best-selling car in Ford’s history, behind only the F-150, Model T and Mustang.
- 1986: Ford of Europe launches the second generation of the Transit van family. Ford Capri ceases production.
- 1987: Ford acquires Aston Martin Lagonda and Hertz Rent-a-Car. Henry Ford II dies at age 70.
- 1988: Ford Festiva, built in Korea by Kia is introduced.
- 1989: Ford acquires Jaguar. Mazda MX-5 Miata is unveiled. Third generation Fiesta is launched in Europe – and establishes itself as the fastest selling generation of Fiesta to date – 1 million units in less than two years. Acquires Associates First Capital Corporation, a finance company. In 1998, it is spun off to Ford shareholders.
- 1990: Ford Aerostar is Motor Trend’s Truck Of The Year, while Lincoln Town Car is Motor Trend’s Car Of The Year. Merkur brand of automobiles production discontinued. Ford of Europe launches fourth generation Escort.
- 1991: Ford Explorer is introduced, turning the traditionally rural and recreational SUV into a popular family vehicle.
- 1992: Ford Aerostar and Ford Taurus/Mercury Sable are redesigned; Ford Taurus becomes America’s top selling car, displacing the Honda Accord. Ford of Europe announces first generation Ford Mondeo, the first product of the global CDW27 platform
- 1992: Redesigned Ford Crown Victoria and Mercury Grand Marquis launched, the first new full-size sedans in 13 years; Ford Country Squire/Mercury Colony Park station wagon discontinued.
- 1993: Ford launches Mondeo in Europe, and announces its North American derivatives – the Ford Contour and Mercury Mystique
- 1994: Ford Tempo and Mercury Topaz are discontinued – replaced by Ford Contour and Mercury Mystique* 1994: Ford Aspire replaces Festiva, becoming the first car in its class to offer standard dual air bags and optional 4-wheel ABS. After large losses, First Nationwide was sold for $1.1 billion to First Madison Bank, which merged while keeping the First Nationwide name.[52]
- 1995: Ford’s first front-wheel-drive V8 sedan is introduced, the 4.6L V8-powered Lincoln Continental. Ford of Europe launches fourth-generation Fiesta. New front-wheel-drive Ford Windstar minivan is introduced. Aerostar remains in production. Redesigned Ford Explorer released, now with standard safety features such as dual air bags, 4-wheel ABS as standard equipment.
- 1996: Ford certifies all plants in 26 countries to ISO 9000 quality and ISO 14001 environmental standards. The V12-powered Jaguar XJS is discontinued. Controversially redesigned «Ovoid» Ford Taurus and Mercury Sable are introduced. Discontinuation of Chevrolet Caprice leaves full size fleet market to Ford Crown Victoria. Ford increases investment stake in a troubled Mazda Corporation to a controlling interest of 33.4%.
- 1997: Full size 4-door SUV Ford Expedition introduced replace the Ford Bronco.Mercury Mountaineer introduced. Redesigned Ford Escort and Mercury Tracer also introduced. Ford Aerostar production ends, along with Ford Probe, Ford Thunderbird, Mercury Cougar, Mazda MX-6, and Ford Aspire, without immediate replacement. Sculpted redesign of Ford’s top-selling F-150 pickup, overcomes controversy to set sales records.
- 1998: Lincoln Navigator creates domestic luxury SUV class. Mark VIII is in its final year, introduces HID-headlamps, midway through model year 1996.
- 1998: The Focus replaces the aging Escort in Europe and quickly becomes one of the best-selling cars of the segment. Is launched in North America for the 2000 model year.
- 1999: Ford acquires Volvo car division from Volvo. Bill Ford becomes chairman of the board, replacing Jacques Nasser. A smaller sporty Mercury Cougar is reintroduced with front-wheel drive. Jaguar Racing Formula One team is formed, with Jackie Stewart at the helm. Ford splits its full-sized pick-ups into two distinct models (the first to do so) with the introduction of the Ford F-Series Super Duty (F-250 – F-550). Ford Excursion (based on Super Duty) is introduced, and has the distinction of being the largest SUV sold anywhere.
- 2000: Ford purchases Land Rover brand from BMW. Lincoln LS and Jaguar S-Type are introduced, along with a refreshed Ford Taurus and Mercury Sable. The Lincoln LS becomes the 2000 Motor Trend Car of the Year. Escort is discontinued in Europe. Third generation Transit platform is launched in Europe.
- 2001: Retro-styled Ford Thunderbird is introduced, based on the Lincoln LS/Jaguar S-Type DEW98 platform, and is also named Motor Trend Car of the Year for 2002.
- 2002: Fifth-generation Fiesta is launched by Ford of Europe.
- 2002: Lincoln Continental is discontinued after a roughly fifty-year run. Jaguar X-Type is introduced (first AWD Jaguar). Escort van production ends in Europe, marking the end of the Escort name after a 24-year production run. Ford Transit Connect production begins at Ford-Otosan in Turkey.
- 2003: Ford Motor Company’s 100th Anniversary. The Ford GT is released, along with limited Centennial editions of some Ford vehicles.
- 2004: Jaguar Racing team sold to Red Bull GmbH. Ranger sales decline, losing the title as top-selling compact pickup. The Ford Escape Hybrid, the first gasoline-electric hybrid SUV, is introduced. Major redesign of the Ford F-150 and introduction of the Lincoln Mark LT. Ford Freestar and Mercury Monterey minivans are introduced, replacing the Ford Windstar and Mercury Villager.
- 2005: Ford Mustang redesigned with retro styling reminiscent of the 1960s models. The Ford Five Hundred, Mercury Montego, and Ford Freestyle are introduced. Mercury Sable production ends, and Ford Taurus production is limited to rental car, taxi, and other fleet sales.
- 2006: Ford Taurus ends production after a 20-year run. Ford Fusion, Mercury Milan, and Lincoln Zephyr introduced. Ford announces major restructuring program The Way Forward, which includes plans to shut unprofitable factories. Bill Ford steps down as CEO, remains as executive chairman. Alan Mulally elected president and CEO. Ford Freestar and Mercury Monterey minivans are discontinued without replacement. Ford mortgages all assets to raise $23.4 billion cash in secured credit lines, in order to finance product development during restructuring through 2009.[43] According to J. D. Power and Associates quality surveys, the Ford Fusion is rated higher in quality than its chief rivals, the Toyota Camry and Honda Accord.[citation needed]
- 2007: Ford sells Aston Martin to a British consortium led by Prodrive chairman David Richards,[citation needed] and announces plans to sell Jaguar and Land Rover. Ford reports losses of $12.7 billion for 2006. Ford Edge and Lincoln MKX introduced. The Lincoln Zephyr is replaced with the Lincoln MKZ. A redesigned Ford Expedition (including the longer wheelbase «EL» version) and Lincoln Navigator are introduced. Ford unveils the Ford Interceptor and Lincoln MKR concept cars, and a pre-production Lincoln MKS is introduced. The Ford Five Hundred, Ford Freestyle and Mercury Montego nameplates are dropped and replaced with the previously retired Ford Taurus, Ford Taurus X, and Mercury Sable nameplates.[53]
- 2008: Ford sells Jaguar and Land Rover to Tata Motors.
- 2008: Ford of Europe launches sixth-generation Fiesta, based on the Verve concept car.[54]
- Sources:
- General Timeline (through 2002): «2002 Annual Report». Ford Motor Company. Archived from the original on 2007-02-17.
- Production figures: U.S. Automobile Production Figures
- 2009 Ford announces that it will leverage more of its European line-up for the North American market. The Turkish-built Transit Connect compact panel van is the first exponent of this strategy, followed by the sixth-generation Ford Fiesta subcompact.
- 2010 Ford sells Volvo Cars to Geely Automobile. Third-generation Ford Focus unveiled – as with the first generation car, it will return to using a single platform for all markets – will be released in North America as a 2012 model.
- 2011: Mercury production ends; the last vehicle is a Grand Marquis. Lincoln Town Car is discontinued. Ford Focus Electric unveiled. Ford announces that they will sell 8 million vehicles globally by 2015.
- 2011: Ford Ranger discontinued for North America; redesigned global version launched.
- 2012: Fourth generation Mondeo/Fusion previewed at the Detroit Motor Show, thus reuniting Ford’s mid-size platform for Europe and North America for the first time since the CDW27 1st gen Mondeo/Contour/Mystique of 1994. Ford Crown Victoria, sold only for export in 2012, is discontinued.
- 2013: Fourth generation Transit/Tourneo launched, along with the second generation Transit Connect and the refreshed Fiesta is revealed.
- 2014: The Ford Mustang celebrates 50 years of production with the launch of its sixth generation. The 2015 F-150 is launched, featuring an aluminum-intensive body design.
- 2017: Ford of Europe launches seventh-generation Fiesta.
- 2018: The 10 millionth Ford Mustang (the top-ranking sports car in America) «gallops off the assembly line.»[55] Ford of Europe launches fourth-generation Focus. Ford announces that it will discontinue all non-SUV and pick-up products in North American markets with the exception of the Mustang.
Criticism and controversies[edit]
Throughout its history, the company has faced a wide range of criticisms. Some have accused the early Fordist model of production of being exploitative, and Ford has been criticized as being willing to collaborate with dictatorships or hire mobs to intimidate union leaders and increase their profits through unethical means.
Ford refused to allow collective bargaining until 1941, with the Ford Service Department being set up as an internal security, intimidation, and espionage unit within the company, and quickly gained a reputation of using violence against union organizers and sympathizers.[56][57]
Ford was also criticized for tread separation and tire disintegration of many Firestone tires installed on Ford Explorers, Mercury Mountaineers, and Mazda Navajos, which caused many crashes during the late 1990s and early 2000s (decade). It is estimated that over 250 deaths and more than 3,000 serious injuries resulted from these failures. Although Firestone received most of the blame, some blame fell on Ford, which advised customers to under-inflate the tires in order to reduce the risk of vehicle rollovers.
Nazi collaboration[edit]
In 1940, at a time when the German division had begun to use slave labor, Ford-Werke was still under the ownership of Dearborn.[24] After Pearl Harbor, Ford lost control of its division in Germany, and all the Ford facilities in Germany came under the full control of the Nazi government. In 1943 the company wrote off all its holdings in Germany as a total loss, and never reclaimed them after the war.[58] The German Ford company used slave labor in Cologne between 1940 and 1945 and produced military vehicles such as trucks, planes, and ships.[24] Many of these allegations were made in a series of United States lawsuits in 1998. The lawsuit was dismissed in 1999 because the judge concluded «the issues … concerned international treaties between nations and foreign policy and were thus in the realm of the executive branch.»[59][60]
Defenders of the company argue that the Ford German division, Fordwerke, had been taken over by the Nazi government after it rose to power, claiming that it was not under the company’s control. Although Ford’s initial motivations were anti-war, the plants in Allied countries were heavily involved in the Allied war effort after the outbreak of war.[60]
Argentine «Dirty War»[edit]
Ford’s Argentine subsidiary was accused of collaborating with the Argentine 1976–1983 military dictatorship, actively helping in the political repression of intellectuals and dissidents that was pursued by said government. No result was proven and the company denied the allegations.
In a lawsuit initiated in 1996 by relatives of some of the estimated 600 Spanish citizens who disappeared in Argentina during the «Dirty War», evidence was presented to support the allegation that much of this repression was directed by Ford and the other major industrial firms. According to a 5,000-page report, Ford executives drew up lists of «subversive» workers and handed them over to the military task-forces which were allowed to operate within the factories. These groups allegedly kidnapped, tortured and murdered workers—at times allegedly within the plants themselves. The company denied the allegations.
In a second trial, a report brought by the CTA, and the testimonies of former Ford workers themselves, claimed that the company’s Argentine factory was used between 1976 and 1978 as a detention center, and that management allowed the military to set up its own bunker inside the plant. The company denied the allegations.[61][62][63]
Ford Pinto[edit]
In September 1971 the Ford Motor Company launched the subcompact Pinto for the North American market. The car’s fuel tank integrity is alleged to have been substandard for the time, making the car inordinately susceptible to fuel tank ruptures in rear impact collisions. An article published in Mother Jones contributed to a public controversy by saying that Ford knowingly released a design that would result in hundreds of deaths as well as calculating that it was cheaper to fight injury claims in court than make changes to the Pinto’s fuel system.[64][65] Public outcry related to the controversy and the Mother Jones article created political pressure on the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration which initialed an investigation. The result of the investigation was the issuing a determination that the Pinto and related Mercury Bobcat were defective. This resulted in Ford recalling 1.5 million Pintos and Bobcats, the largest automotive recall to date.[66][67] Two notable legal cases, Grimshaw v. Ford Motor Company and State of Indiana v. Ford Motor Company are the result of accident related fuel system fires. The Grimshaw jury awarded the plaintiffs $127 million, the largest product liability and negligence award in history at that time; the trial judge reduced the jury award to $3.5 million.[65] Indiana v. Ford was the first time a corporation indicted on criminal charges for a defective product, the Ford Pinto, and the first corporation charged with reckless homicide. The case resulted in a not guilty verdict.[66] Subsequent research has discredited early fatality figures and indicate the Pinto’s overall fire safety record was typical for subcompacts of the time.[65]
References[edit]
- ^ «Historic Henry Ford home». Mac’s Motor City Garage. Archived from the original on 2016-09-21. Retrieved 2016-07-28.
- ^ a b c d e f Barnard, Harry (2002). Independent Man: The Life of Senator James Couzens. Wayne State University Press. ISBN 1104834677.
- ^ Miller, James Martin; Ford, Henry (1922). The Amazing Story of Henry Ford. M. A. Donohue & Co. p. 72.
- ^ a b c Clymer (1950), p. 120.
- ^ Clymer (1950), p. 104.
- ^ Clymer (1950), p. 63.
- ^ a b Clymer (1950), p. 32.
- ^ Clymer (1950), p. 51.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Georgano, G.N. (1985). Cars: Early and Vintage, 1886–1930. London: Grange-Universal.
- ^ Clymer (1950), p. 147.
- ^ Horvath, Dennis N. «Ford Motor Company Announces $5 a Day Minimum Wage for an Eight hour shift». Autogiftgarage.com. Archived from the original on 28 October 2014. Retrieved 20 June 2014.
- ^ a b Henry Ford, Biography (March 25, 1999). A&E Television.
- ^ «History of Ford in Argentina». Auto-historia.com. Archived from the original on 9 August 2007. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- ^ «Ford in South Africa». Dynaconsult.
- ^ Hyde, Charles K. (2005). The Dodge Brothers: The Men, the Motor Cars, and the Legacy. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-81433-246-7.
- ^ «Henry Ford And The Model T – Forbes Greatest business stories of all time». Wiley. 1996.
- ^ myFord magazine, Fall 2006.
- ^ «History». Ford Motor Company. Archived from the original on 2007-02-13.
- ^ Reed, Drew (August 19, 2016). «Lost cities #10: Fordlandia – the failure of Henry Ford’s utopian city in the Amazon». The Guardian.
- ^ Arnesen, Eric (2004). The Human Tradition in American Labor History. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 234. ISBN 0-8420-2987-7.
- ^ Babson, Steve (1986). Working Detroit: The Making of a Union Town. Wayne State University Press. p. 59. ISBN 0-8143-1819-3.
- ^ Tzouliadis, Tim (2008). The Forsaken: An American Tragedy in Stalin’s Russia. Penguin Press. ISBN 978-1-59420-168-4.
Many of the slain were dumped in the mass grave at Yuzhnoye Butovo District near Moscow.
- ^ Tzouliadis, Tim (2008). The Forsaken: An American Tragedy in Stalin’s Russia. Penguin Press. ISBN 978-1-59420-168-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Wallace (2003).
- ^ Michigan History, January/February 1993
- ^ Baldwin, Neil. (2001). Henry Ford and the Jews. New York: Public Affairs.
- ^ a b c Dobbs, Michael (November 30, 1998). «Ford and GM Scrutinized for Alleged Nazi Collaboration». The Washington Post.
- ^ Baime (2014), p. 24, 88 & 218.
- ^ Baime (2014).
- ^ Peck, Merton J. & Scherer, Frederic M. (1962). The Weapons Acquisition Process: An Economic Analysis. p. 619.
- ^ «Ford GPW». National Museum of World War II Aviation, Colorado Springs. Retrieved May 18, 2022.
- ^ «About Ford GPW». kaiserwillys.com. Retrieved May 18, 2022.
- ^ «On this day in motoring — Wednesday 20th August 1941».
- ^ «Merlin Engines In Manchester». BBC History. 2005. Retrieved May 18, 2022.
- ^ a b c Yates, Brock. «10 Best Moguls». Car and Driver. Vol. 88, no. 1. p. 49.
- ^ a b Lochbiler, Don (July 22, 1997). «Michigan History: ‘I Think Mr. Ford is Leaving Us’«. The Detroit News. Archived from the original on 2012-07-15. Retrieved March 1, 2011.
- ^ a b Flory (2008), p. 701.
- ^ Flory (2008), p. 808.
- ^ Meggs, Philip; Purvis, Alston (1983). Meggs’ History of Graphic Design. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Inc. pp. 374–377, 379, 382, 390, 404–407, 435 & 477. ISBN 0-471-69902-0.
- ^ Wallace (2003), p. 333.
- ^ Bradsher, Keith (15 April 2000). «Ford Motor to Pay $10 Billion Dividend and Ensure Family Control». The New York Times.
- ^ «Ford considers going private». Reuters. August 24, 2006.[dead link]
- ^ a b «Ford Finalizes Financing Package». The Washington Post. 15 December 2006.
- ^ Szczesny, Joseph R. (2009-09-15). «For Ford, Going It Alone Looks Like a Good Strategy». Time. Archived from the original on September 22, 2009. Retrieved 2010-04-10.
- ^ Fontevecchia, Agustino (19 March 2013). «U.S. Companies Stashing More Cash Abroad As Stockpiles Hit Record $1.45T». Forbes.
- ^ «Cash Pile Grows 10% to $1.45 Trillion; Overseas Holdings Continue to Expand». Moody’s Investors Service.
- ^ «Announcement: Moody’s: US companies’ cash pile grows 10% in 2012, to $1.45 trillion». Global Credit Research. New York. 18 March 2013.
- ^ Ford, Henry & Crowther, Samuel (1922). «Chapter XII: Money – Master or Servant?». My Life and Works. London, UK: William Heinemann & Co. – via Project Gutenberg.
- ^ Roberts, Sam (2001). Ford Model Y. Veloce Publishing PLC. ISBN 1-901295-88-5.
- ^ «Ford’s 50th anniversary show was milestone of ’50s culture». Palm Beach Daily News. December 26, 1993. p. B3 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ Furlong, Tom (August 2, 1985). «Ford Motor to Acquire First Nationwide for $493 Million in Cash». Los Angeles Times. Retrieved December 6, 2020.
- ^ Kraul, Chris; Nauss, Donald W. (April 15, 1994). «Ford to Sell Unprofitable Thrift Unit to Dallas Firm». Los Angeles Times. Retrieved December 6, 2020.
- ^ «2008 Ford Taurus». Ford Motor Company.
- ^ «Ford Announces Agreement To Sell Aston Martin» (Press release). Ford Motor Company. 2007-03-12. Archived from the original on 2007-10-11.
- ^ «Mustang milestone: 10 millionth ‘Stang gallops off assembly line». The ClassicCars.com Journal. 9 August 2018. Retrieved 7 November 2018.
- ^ «Ford Motor Company Chronology: Battle of the Overpass, May 26, 1937». The Henry Ford. 2010. Archived from the original on 2011-06-08.
- ^ «The Battle of the Overpass». The Detroit News. Archived from the original on 2013-01-02.
- ^ Brinkley (2003), p. 542.
- ^ «Ford and GM scrutinized for Alleged Nazi Collaboration». The Washington Post. November 30, 1998. Archived from the original on January 17, 1999.
[After December 1941] … At GM and Ford plants in Germany, reliance on forced labor increased.
- ^ a b Reich, Simon (2000). «The Ford Motor Company and the Third Reich». Dimensions: A Journal of Holocaust Studies. Anti-Defamation League. 31 (2). Archived from the original on 2011-01-10. Retrieved 2010-12-26.
- ^ «Argentina checks Ford’s ‘military ties’«. BBC News. 2002-11-06. Retrieved 2010-01-04.
- ^ «Ford sued over Argentine abuses». BBC News. 2006-02-24. Retrieved 2010-01-04.
- ^ Vann, Bill (20 March 1998). «Ford complicit in Argentine repression». WSWS. Archived from the original on July 25, 2008.
- ^ Dowie, Mark (September–October 1977). «Pinto Madness». Mother Jones. Retrieved 2009-02-27.
- ^ a b c Schwartz, Gary T. (1990). «The Myth of the Ford Pinto Case». Rutgers Law Review. 43: 1013.
- ^ a b Lee, Matthew T.; Ermann, M. David (February 1999). «Pinto «Madness» as a Flawed Landmark Narrative: An Organizational and Network Analysis». Social Problems. 46 (1): 30–47. doi:10.2307/3097160. JSTOR 3097160.
Eventually, NHTSA acted to restore its credibility as the nation’s traffic safety enforcer in the face of criticism over its initial inaction on the Pinto issue by forcing the largest automotive recall at the time.
- ^ Jones, William H. (June 10, 1978). «Ford Recalls 1.5 Million Small Cars. Ford Recalls 1.5 Million Pintos, Bobcats, Pintos, Bolcats Face Alteration To Cut Fire Risk». The Washington Post. Retrieved March 4, 2016.
Ford Motor Co. yesterday recalled 1.5 million Pinto and Mercury Bobcat cars, to make alterations that will reduce the risk of fuel tank fires in rear-end accidents.
Bibliography[edit]
- Arnold, Horace Lucian & Faurote, Fay Leone (1915). Ford methods and the Ford shops. Preface by Charles Buxton Going. The Engineering Magazine Company. OL 13554528M.
- Baime, A.J. (2014). The Arsenal of Democracy: FDR, Detroit, and an Epic Quest to Arm an America at War. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN 978-0-54771-928-3.
- Batchelor, Ray (1994). Henry Ford: Mass Production, Modernism and Design. Manchester, UK: Manchester University Press. ISBN 978-0-71904-174-7.
- Bayou, M. E. & De Korvin, A. (December 2008). «Measuring the leanness of manufacturing systems – a case study of Ford Motor Company and General Motors». Journal of Engineering and Technology Management. 25 (4): 287–304. doi:10.1016/j.jengtecman.2008.10.003.
- Brinkley, Douglas (2003). Wheels for the World: Henry Ford, his company, and a century of progress, 1903–2003. New York: Viking Press. ISBN 978-0-67003-181-8.
- Bryan, Ford R. (1990). Beyond the Model T: The Other Ventures of Henry Ford. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. ISBN 978-0-81432-236-9.
- Bryan, Ford R. (1993). Henry’s Lieutenants. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. ISBN 0-8143-2428-2.
- Clymer, Floyd (1950). Treasury of Early American Automobiles, 1877–1925. New York: Bonanza Books.
- Dempsey, Mary A. (1994). «Fordlandia». Michigan History. Vol. 78, no. 4. pp. 24–33. Ford’s rubber plantation in Brazil.
- Di Minin, Alberto, et al. «Technological Discontinuities and Dominant Designs: The Case of Ford, 1896-1914.» Academy of Management Proceedings. Vol. 2019. No. 1. (2019) online
- Flory, J. «Kelly», Jr. (2008). American Cars 1946–1959. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Co. ISBN 978-0-78643-229-5.
- Grandin, Greg (2010). Fordlandia: The Rise and Fall of Henry Ford’s Forgotten Jungle City. London, UK: Icon. ISBN 978-1-84831-147-3.
- Holden, Len (January 2005). «Fording the Atlantic: Ford and Fordism in Europe (Review of Hubert Bonin, Yannick Lung & Steve Tolliday (eds), Ford, 1902–2003:The European History, Paris: Plage, 2003, 2 Vol Boxed Set, ISBN 2-914369-06-9)». Business History. 47 (1): 122–127. doi:10.1080/0007679042000267505. S2CID 155073806.
- Hounshell, David A. (1984), From the American System to Mass Production, 1800–1932: The Development of Manufacturing Technology in the United States, Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press, ISBN 978-0-8018-2975-8, LCCN 83016269, OCLC 1104810110
- Jacobson, D. S. (1977). «The Political Economy of Industrial Location: the Ford Motor Company at Cork 1912–26». Irish Economic and Social History. 4 (4): 36–55. doi:10.1177/033248937700400103. JSTOR 24337019. S2CID 157765884. Ford and Irish politics.
- Lazdowski, Yvette J. Persistence and Vigilance: A View of Ford Motor Company’s Accounting over its First Fifty Years (Emerald Publishing Limited, 2020). excerpt
- Lewis, David L. (1980). «Ford and Kahn». Michigan History. Vol. 64, no. 5. pp. 17–28. Ford commissioned architect Albert Kahn to design factories.
- Lewis, David L. (1993). «Working Side by Side». Michigan History. Vol. 77, no. 1. pp. 24–30. Why Ford hired large numbers of black workers.
- Lewis, David L. (1995). «Henry Ford and His Magic Beanstalk». Michigan History. Vol. 79, no. 3. pp. 10–17. On Ford’s interest in soybeans and plastics.
- McIntyre, Stephen L. (2000). «The Failure of Fordism: Reform of the Automobile Repair Industry, 1913–1940». Technology and Culture. 41 (2): 269–299. doi:10.1353/tech.2000.0075. S2CID 109379833. Repair shops rejected flat rates.
- Meyer, Stephen (1981). The Five Dollar Day: Labor Management and Social Control in the Ford Motor Company, 1908–1921. Albany, NY: State University of New York Press. ISBN 978-0-87395-508-9.
- Di Minin, Alberto, Giulio Ferrigno, and Alberto Zordan. «Technological Discontinuities and Dominant Designs: The Case of Ford, 1896-1914.» Academy of Management Proceedings. Vol. 2019. No. 1. Briarcliff Manor, NY 10510: Academy of Management, 2019.
- Nevins, Allan & Hill, Frank Ernest (1954). Ford: the Times the Man the Company. New York City: Charles Scribner’s Sons.; the most detailed scholarly study
- Nevins, Allan & Hill, Frank Ernest (1957). Ford: Expansion and Challenge, 1915–1933. New York City: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
- Nevins, Allan & Hill, Frank Ernest (1963). Ford: Decline and Rebirth, 1933–1962. New York City: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
- Nolan, Mary (1994). Visions of Modernity: American Business and the Modernization of Germany. New York: OUP. ISBN 978-0-19508-875-5.
- Raff, Daniel M. G.; Summers, Lawrence H. (October 1987). «Did Henry Ford Pay Efficiency Wages?» (PDF). Journal of Labor Economics. 5 (4): S57–S86. doi:10.1086/298165. S2CID 158557619.
- Pietrykowski, Bruce (1995). «Fordism at Ford: Spatial Decentralization and Labor Segmentation at the Ford Motor Company, 1920–1950». Economic Geography. 71 (4): 383–401. doi:10.2307/144424. JSTOR 144424.
- Pool, James; Pool, Suzanne (1978). «Ford and Hitler». Who Financed Hitler: The Secret Funding of Hitler’s Rise to Power, 1919–1933. New York City: Dial Press. ISBN 978-0-70881-756-8.
- Roe, Mark J. «Dodge v. Ford: What Happened and Why?.» Vanderbilt Law Review 74 (2021): 1755+ online
- Roediger, David (1988). «Americanism and Fordism – American Style: Kate Richards O’Hare’s ‘Has Henry Ford Made Good?’«. Labor History. 29 (2): 241–252. doi:10.1080/00236568800890141. Socialist praise for Ford in 1916.
- Segal, Howard P. (1988). «‘Little Plants in the Country’: Henry Ford’s Village Industries and the Beginning of Decentralized Technology in Modern America». Prospects. 13: 181–223. doi:10.1017/S0361233300006724. Ford created 19 rural workplaces as pastoral retreats.
- Shook, Robert L. (1990). Turnaround: The New Ford Motor Company. New York City: Prentice Hall Press. ISBN 978-0-13932-062-0.
- Tedlow, Richard S. (1988). «The Struggle for Dominance in the Automobile Market: the Early Years of Ford and General Motors». Business and Economic History. 17: 49–62. JSTOR 23702960. Ford stressed low price based on efficient factories but GM did better in oligopolistic competition by including investment in manufacturing, marketing, and management.
- Thomas, Robert Paul (1969). «The Automobile Industry and its Tycoon». Explorations in Entrepreneurial History. 6 (2): 139–157. Argues Ford did NOT have much influence on US industry.
- Valdés, Dennis Nodin (1981). «Perspiring Capitalists: Latinos and the Henry Ford Service School, 1918–1928». Aztlán. 12 (2): 227–239. Ford brought hundreds of Mexicans in for training as managers.
- Wallace, Max (2003). The American Axis: Henry Ford, Charles Lindbergh, and the rise of the Third Reich. New York City: St. Martin’s Press. ISBN 978-0-31229-022-1.
- Watts, Steven (2005). The People’s Tycoon: Henry Ford and the American Century. New York City: A.A. Knopf. ISBN 978-0-37540-735-2.
- Wilkins, Mira; Hill, Frank Ernest (1964). American Business Abroad: Ford on Six Continents. Detroit: Wayne State University Press.
- Williams, Karel; Haslam, Colin & Williams, John (1992). «Ford versus ‘Fordism’: The Beginning of Mass Production?». Work, Employment & Society. 6 (4): 517–555. doi:10.1177/095001709264001. S2CID 154726310. Stress on Ford’s flexibility and commitment to continuous improvements.
С этой статьи я начинаю новую рубрику в блоге “Мой рубль”, которая будет называться Истории успеха выдающихся компаний. В этой рубрике мы будем изучать историю создания и развития известных мировых брендов. Будем разбираться, что помогло великим компаниям стать таковыми, что стоит в основе их миссии и ценностей. Какие принципы успеха были заложены в них основателями и т.д.
Я молодой предприниматель, у меня несколько бизнес-проектов и мне хочется, чтобы эти проекты выросли и стали не менее выдающимися, чем те компании, которые будут разбираться в данной рубрике.
Чтобы это сделать я решил не выдумывать велосипед, а пойти по стопам великих. И начнем мы с компании Ford Motor Company, или в простонародье Форд.
Иди вперед – слоган легендарного бренда Ford Motor Company. Чтобы понять, какой смысл вкладывают в это понятие фордовцы, посмотрите короткий, но весьма эффектный промо-ролик ниже:
Компания Ford Motor занимает второе место по объему выпуска автомобилей в Европе, третье на рынке США и четвертое в мире. Под брендом «Ford» компания выпускает модели легковых и коммерческих автомобилей, также ей принадлежит и торговая марка «Lincoln».
Предприятия легендарной американской автомобилестроительной компании расположены на территории 65 стран – в США, Канаде, Аргентине, Испании, Китае, России и др.
Общее количество занятых в Ford Motor сотрудников составляет около 171 000 человек. Продажи компании за 2012 г. составили более 130 млрд. долларов!
В списке крупнейших публичных обществ, по версии журнала Forbes, Ford Motor Company занимает 4 место в своей отрасли, уступая тройке лидеров — немецким компаниям Volkswagen Group и Daimler (1-ое и 3-е места) и японской Toyota Motor.
Ford Motor является одной из крупнейших компаний в мире, управляемой одной семьей – Фордам принадлежит около 40% акций. Ценные бумаги компании, находящиеся в свободном доступе, торгуются на Нью-Йоркской фондовой бирже (NYSE). Стоимость одной акции — около 2$ (апрель 2013г.).
По данным Forbes рыночная капитализация компании в 2013 г. достигла более 51 млрд. долларов!
Но история Ford Motor занимательна не только финансовыми показателями, но и интересными фактами. Именно эта компания впервые применила классический автосборочный конвейер, и в этом, безусловно, заслуга ее легендарного основателя Генри Форда.
В 2013 году компания празднует свое 110-летие, а ведь этот срок превышает длительность жизни среднестатистического человека! Ford Motor Company – настоящий динозавр автомобилестроения.
В чем заключается ее секрет долгожительства и успеха? Попробуем разобраться
Штаб-квартира компании находится в городе Дирборн (штат Мичиган), там, где 30 июля 1863 года появился на свет ее основатель. Как говорят, где родился – там и пригодился, в 2013 году исполняется 150 лет со дня рождения Генри Форда, а дело всей его жизни по-прежнему развивается и процветает.
Сейчас «у руля» современного автомобилестроения стоит Вильям Форд-младший — правнук Генри Форда, являющийся Председателем совета директоров Ford Motor. В 2001 году он возглавил компанию, убытки которой на тот момент составляли около 5 млрд. долларов.
Форд-мл. смог привести ее к трем годам рентабельности, к тому же именно он пригласил на должность президента компании Алана Малалли, талантливого управленца, сумевшего найти правильную стратегию компании в 3-ем тысячелетии.
Конкурентоспособные расходы, высокое качество, польза для общества – вот основные принципы управления компанией, которые завещал Генри Форд, и его потомок по сей день руководствуется формулой успеха прадеда.
Эти мысли я уже взял на вооружение. Например, одно из моих направлений – это обучение и предоставление образовательных и консалтинговых услуг. Мне есть над чем здесь поработать. Я хочу сделать так, чтобы у меня были самые качественные услуги.
Это вопрос требующий серьезной проработки. Я постоянно задаюсь вопросом: “Как сделать свои услуги более качественными? Как лучше обслужить клиента? Что еще я могу сделать для того, чтобы человек получал больше за ту же цену?”
В другом проекте (интернет-магазин mistersaver.ru) я тоже стараюсь применить эти принципы. Уже само направление энергосберегающих технологий было выбрано мной за то, что здесь можно оказать пользу обществу. За высокое качество товаров я, к сожалению, не могу ответить, так как я не производитель. Но все равно стараюсь снизить риски своих клиентов.
Например, у нас есть 45-дневный тест-драйв продуктов. В течение этого времени клиент может попробовать предлагаемые нами решения и если они его разочаруют, то мы возвращаем деньги.
В общем, при постановке перечисленных выше вопросов можно придумать много интересных решений. Но давайте вернемся к Фордам.
Как же начиналась история семейного предприятия?
Компания Ford Motor была основана в 1903 году, предпринимателями Мичигана, возглавляемыми Генри Фордом, на долю которого приходилось 25,5% акций вновь созданного предприятия. Под автомобильный завод была переоснащена фургонная фабрика в Детройте.
Под руководством Форда, являющегося одновременно и вице-президентом, и главным инженером, работники собирали автомобили из поставляемых другими заводами запчастей. Уже в июле 1903 года Ford Motor Company продала свой первый автомобиль.
В то время компания собирала автомобили только «под заказ», и Форд столкнулся с нехваткой квалифицированных рабочих для выпуска машин «ручной сборки». Он решил стандартизировать детали автомобиля, чтобы их могли собирать даже не специалисты.
В 1908 году завод выпускает модель «Форд-T» – надежный и недорогой автомобиль. Форд внедряет в цехах беспрерывную линию по сборке «Форда-Т»; благодаря конвейерным линиям, производство автомобилей достигает рекордного уровня – новая машина сходит с конвейера каждые 10 секунд! Инновации в Ford Motor служат отправной точкой для развития массового производства во всем мире.
Продукт компании Ford «Форд-Т» подстегивает экономику Америки — в 1909 году власти сооружают бетонный участок длиной в милю на улице в Детройте, что положило начало массовому строительству дорог.
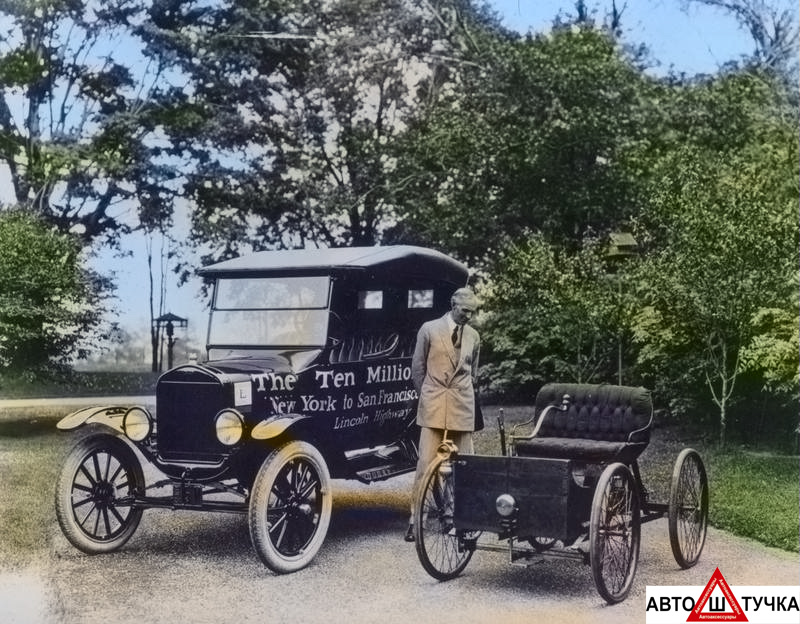
В 2008 году в Ричмонде (штат Индиана) в рамках 100-летнего юбилея автомобиля «Форд-Т» прошла вечеринка «T-Party», поставившая себе целью войти в Книгу рекордов Гиннеса по количеству принявших в ней участие машин именно этой модели. По приблизительным подсчетам, из 15 млн. автомобилей, выпущенных компанией с 1908 по 1927 гг., на сегодняшний день сохранилось почти сто тысяч машин!
На свой праздник некоторые «Форды-Т» попали своим ходом – один из «юбиляров» пробежал на своих четырех колесах почти 3000 км! Вот вам и музейный экспонат! Такому «забегу» может позавидовать и современное авто.
В 1999 году более 120 экспертов из 32 стран по праву назвали «Форд-Т» самым значимым автомобилем ХХ столетия!
В 1919 году Генри Форд и его сын Эдсел выкупают акции предприятия у других акционеров и становятся единоличными владельцами Ford Motor. В том же году Эдсел наследует управление компанией.
В 1927 году, когда продажи любимого, но уже морально устаревшего «Форда-Т» не приносят прибыли, Форд приостанавливает производство и приступает к созданию нового автомобиля. В 1927 году он представляет новую модель «Форд-А», выгодно отличавшуюся своим дизайном и техническими параметрами.
Со вступлением США во Вторую мировую войну, Ford Motor начинает выпускать джипы и грузовики для армии — компании «простили» пронацистские симпатии ее основателя, когда в 30-х гг. в Германии Форд организовал производство гусеничной и колесной техники для Вермахта.
В 1943 году, после скоропостижной смерти сына, Генри Форд вновь возвращается на пост президента, а в сентябре 1945 года передает полномочия своему старшему внуку – Генри Форду II.
Со смертью основателя компании в 1947 году, для Ford Motor заканчивается определенная эпоха. Но, не смотря на кончину своего легендарного идейного вдохновителя, компания продолжает активно развиваться
Сегодня «Ford» является одним из самых известных брендов планеты, а знаменитый овальный логотип компании существует уже более полстолетия! Фирменная эмблема Ford Motor менялась несколько раз. Первый логотип придумал помощник Генри Форда, но уже через несколько лет он преобразился, в 1906 году торговый знак приобрел новые черты — «летящее» написание первой и последней букв названия компании подчеркивало стремительное движение вперед.
В 1907 году, благодаря английским представителям компании, появляется овальный логотип, символизирующий «клеймо высшей пробы» — экономичность и надежность.
В 1911 году эмблема компании окончательно утвердилась – овальная форма логотипа была соединена с «летящим» написанием. Первым автомобилем с этим знаком на решетке радиатора была модель «Форд-A».
С 1976 года эмблема Ford в виде овала с синим фоном и серебряными литерами ставится на все автомобили компании.
В 2003 году, в честь 100-летнего юбилея Ford Motor, дизайн известного фордовского знака был немного изменен – логотипу придали черты самых первых, исторических, эмблем.
Впрочем, в XXI веке редизайном логотипа компания не ограничилась. Большим изменениям подверглась стратегия компании
Ранее Ford Motor по географическому признаку разделялся на три структуры: Ford North Americа, Ford Asia Pacific и Ford of Europe. Каждое из этих подразделений имело свой модельный ряд, для автомобилей региональных рынков применялись разные технические решения и дизайн.
Однако президент компании Алан Малалли, возглавивший Ford Motor в сентябре 2006 года, в этом же году объявляет о новом стратегическом направлении «Единый Ford» («One Ford»). Смена стратегии требовалась, дабы уберечь компанию от разорения – ее убытки на тот момент составляли около 17 млрд. долларов.
Ключевая идея «Единого Ford» заключалась в том, что компания постепенно начинает выпускать автомобили, общие для всех рынков — мир становится глобальным и ему требуются глобальные автомобили. Примером такой «всемирной» машины стал Ford Focus III, построенный на единой платформе.
В рамках новой стратегии, компания продает свои люксовые марки — Aston Martin, Jaguar, Volvo. Во время кризиса требовалось сделать компанию проще, а поскольку 85% ее бизнеса обеспечивалось брендом Ford, все силы и средства бросаются именно на его спасение.
В 2010 году компания выпускала около 45 моделей машин; по словам президента компании, эту цифру планируется сократить до 20-25.
Для объединения региональных подразделений компании в «Единый Ford», Малалли сумел реконструировать информационное подразделение и поднять его авторитет: впервые в истории Ford Motor директор IT-департамента вошел в совет директоров и начал подчиняться непосредственно гендиректору.
Экономический кризис смог пережить и завод в Дирборне, родном городе Генри Форда. Ранее предприятие простаивало неделями, но грамотное руководство и выпуск пикапов Ford Focus F150 позволили заводу пережить нелегкие времена без государственных вливаний.
Завод в Дирборне просто огромен — его площадь составляет около 220 000 м2, а от начала до конца сборочной линии тянется почти 7 км конвейеров, извивающихся по предприятию, как гигантские американские горки. В настоящее время на заводе ежедневно собирается около 1200 автомобилей, в каждом из которых более 3 тысяч различных запчастей.
К слову о запчастях, вспоминается анекдот: «В связи с необходимостью увеличить долю российских комплектующих в автомобилях Ford Focus, компания Ford решила увеличить число резиновых ковриков до восьми».
Мне кажется, что если руководствоваться в работе принципом Генри Форда — «качество — это делать что-либо правильно, даже когда никто не смотрит» — то наверняка будет что предложить и помимо ковриков )
В 3-ем тысячелетии Ford Motor активно меняется, его слоганы трансформируются вместе с ним. Первый рекламный девиз, появившийся в 1914 году, гласил «Ford: The Universal Car» («Форд: универсальный автомобиль»).
Среди особо удачных рекламных девизов стоит отметить такие, как «Навстречу переменам» и «Надежен. Создан для жизни»
Сейчас на смену слоганам в Северной Америке («Drive One» / «Возьми и езжай») и Европе («Feel the Difference» / «Почувствуй разницу») пришла глобальная формула продвижения «единого форда», звучащая как «Go futher» / «Иди вперед».
Впервые этот призыв появился в новогоднем поздравлении главы Ford, адресованном всему персоналу. Единый слоган теперь будет звучать на всех рекламных материалах компании.
Между прочим, коллектив компании сильно замотивирован на превосходный результат; и если Антон Чехов был убежден, что «в человеке всё должно быть прекрасно: и лицо, и одежда, и душа, и мысли», то специалисты Ford Motor убеждены, что в автомобиле тоже должно быть все прекрасно – от топливной технологии до дизайна салона.
Чтобы гарантировать отличный внешний вид своей продукции, в компании существует специальная лаборатория The Visual Performance Evaluation Lab.
В лаборатории расположены около 300 лампочек общей мощностью 6кВт, с помощью которых моделируются различные фазы обращения земли вокруг Солнца. Может возникнуть резонный вопрос – какое отношение имеет светило к развитию фордовских транспортных средств?
Дело в том, что внешний вид машины и ее интерьер изменяется в зависимости от освещения и времени суток; чтобы отследить эти перемены и минимизировать нежелательные эффекты (к примеру, отблики на панели приборов), компания и проводит подобные тесты. Посмотреть, как работает лаборатория, можно здесь:
Компания Ford Motor принимает активное участие в спортивных соревнованиях по всему миру. Главным направлением ее деятельности в сфере автоспорта является чемпионат «Формула Ford», выделяющийся среди гоночных соревнований для одноместных автомобилей своей долгой и интересной историей.
С момента своего появления в 1967 году, «Формула Ford» стала настоящей «кузницей кадров» — именно в ней приобретали опыт такие впоследствие прославленные автогонщики как Джеймс Хант, Дженсон Батон, Айртон Сенна, Мика Хаккинен, Михаэль Шумахер и др.
Компания тесно связана с гонками «Формула-1»: она поставляла двигатели для гоночных автомобилей этой серии на протяжении 4 десятков лет, с 1967 по 2004 гг. А доработанная модель Ford GT стала самым быстрым автомобилем в мире, который может ездить по дорогам общего пользования – достигнув скорости 455,80 км/ч, он был внесен в Книгу рекордов Гиннеса.
Ford Motor также участвует в Чемпионате мира по ралли с момента его основания, с 1973 года, и имеет собственную раллийную команду.
От себя хочу добавить, что я бы очень хотел создать такой бизнес, который стал бы для меня и сотрудников не только работой, но и интересным увлечением. Прикольно заниматься чем-то не только ради денег, но и ради удовольствия, адреналина, красоты, изящества и т.д.
Ford GT – крутая тачка. Я бы с удовольствием на ней прокатился. А еще лучше поучаствовал в соревнованиях. Я азартный человек. Спортом занимаюсь с детства. И мне нравится чувство соревновательности и дух победы!
Компания может похвастаться не только скоростными характеристиками своих автомобилей, но и их объемами продаж. В 2012 году аналитическое агентство JATO Dynamics назвало автомобиль Ford Fiesta вторым самым продаваемым автомобилем в Европе
Что касается российского рынка, то тут компания Ford в 2006 году становится лидером продаж среди иностранных брендов. История Ford Motor в России начинается еще в 1907 году; после революции 1917 г. она продолжила свою деятельность на нашей территории.
В конце 20-х гг. с руководством СССР был заключен контракт, согласно которому американцы предоставляли чертежи двух автомобилей, свою помощь в строительстве автозавода и обучении рабочих. Первые автомобили нового завода в Нижнем Новгороде — ГАЗ-А и ГАЗ-АА — были лицензионными «клонами» машин компании «Форд».
В 1996 году открывается торговое представительство Ford в Москве. Дочерней компании Ford Motor в РФ принадлежит автомобильный завод во Всеволожске (Ленинградская область), открытый в 2002 году. На предприятии осуществляется сварка кузовов, покраска и финальная сборка машин Ford Focus III и Ford Mondeo (с 2009 года). В апреле 2006 года этот завод выпустил стотысячный автомобиль Ford Focus.
В течение 2007 года в России было продано более 175 000 автомобилей марки «Форд», около 90 000 из которых пришлось на модель Focus.
Отметить успех автомобиля Focus, хорошо продаваемого не только в России, компания решила весьма оригинально – заказав ледяную скульптуру своего авто в масштабе 1:1.
Масса ледяной машины превысила 6 тонн, что больше пяти масс настоящих Ford Focus (снаряженная масса авто равняется 1,3 тоннам). Это прозрачное изваяние демонстрировалась на международной автомобильной выставке British International Motor Show.
Впрочем, свою миссию Ford Motor видит не только в получении больших прибылей от продаж.
Компания сосредоточена на создании сильного бизнеса, выпускающего продукцию, которая улучшает мир. Свое пафосное заявление Ford Motor подкрепляет вполне конкретными делами. Компания занимает активную позицию в области охраны окружающей среды, в области экологичных технологий ее можно назвать настоящим первопроходцем.
В европейских автомобилях Ford используется более 250 неметаллических компонентов, содержащих переработанные материалы, что позволяет ежегодно отправлять на свалки на 14 000 тонн меньше отходов.
Ford Motor разрабатывает бензиновые и дизельные двигатели, позволяющие еще больше экономить топливо. Новый Ford Mondeo, к примеру, оснащен дизельным двигателем объемом 1,8 литра и является более экономичным, чем эта же модель 1993 года, производя на 20% меньше углекислого газа.
Уже сегодня компания предлагает широчайший выбор экологичных автомобилей. Любой водитель знает, что транспортное средство и алкоголь — вещи несовместимые. Однако под капотом автомобилей Ford Flexifuel и Ford C-MAX Flexifuel эти понятия «подружились» — ведь они работают не на бензине, а на топливе E85, на 85% состоящем из спирта биэтанола.
Биоэтанол получают из таких натуральных продуктов, как древесные отходы, пшеница, сахарная свекла и пр., т.е. из возобновляемого сырья. Данная топливная технология снижает выбросы CO2 в атмосферу по сравнению с бензиновыми двигателями на 30-80%, поэтому подобные модели Ford Motor можно смело называть «зелеными» автомобилями.
Еще одной гордостью Ford Motor является автозавод в Дагенхеме (юго-восток Великобритании) – это первое в мире предприятие, чьи производственные мощности целиком и полностью обеспечиваются электроэнергией, полученной от собственных ветряных турбин.
Но на этом Ford Motor не собирается останавливаться. Следуя своему лозунгу «иди вперед», компания продолжает ставить перед собой все новые и новые цели.
Не нужно зацикливаться на деньгах!
Из перечисленного выше можно сделать вывод, что при создании и развитии бизнеса нельзя зацикливаться только на деньгах и прибылях. Бизнес, который вы развиваете должен помогать людям, должен улучшать нашу жизнь, делать ее более комфортной и безопасной.
Мне нравится политика компании Форд, относительно экологичности производимых ими автомобилей, а также экономичности при эксплуатации. В моем блоге можно найти массу материалов о том, как сократить свои расходы. Я сам в свое время установил на свой автомобиль газобаллонное оборудование, чтобы тратить меньше денег на бензин.
Именно разумное потребление лежит в основе моего видения того, как достичь финансовой свободы и независимости. Чтобы увеличить свои доходы нужно сделать так, чтобы доходы всегда были ваших расходов. А полученную разницу (остаток), нужно направлять на создание активов, накапливание денег, чтобы впоследствии создать бизнес, например.
Спасибо компании Ford Motor за то, что еще раз убедили меня в правильности выбранного пути и за то, что показали каким должен быть правильный бизнес.
- Статья опубликована 06.07.2014 07:34
- Последняя правка произведена 23.02.2017 05:04
| Полное название: | Ford Motor Company. |
| Другие названия: | Ford (Форд) |
| Существование: | 1903 г. — наши дни |
| Расположение: |  США: Дирборн, штат Мичиган. США: Дирборн, штат Мичиган. |
| Ключевые фигуры: | Вильям Форд мл. (председатель совета директоров) Алан Малалли (президент). |
| Продукция: | Легковые и коммерческие автомобили: Ford |
| Модельный ряд: |
Ford Mondeo Ford Kuga Ford Airstream Ford GT (2003) Ford Windstar Ford Ka Ford Flex Ford Explorer Ford Orion Ford Probe Ford Excursion Ford Edge Ford Cougar Ford C-Max Ford Crown Victoria Ford EcoSport Ford Fiesta Ford Five Hundred Ford Capri |
Генри Форд (Henry Ford) – величайшая личность в истории автомобилестроения.
Когда-то именно он, будучи еще мальчишкой, работая на ферме своего отца, шлепнулся сильно с лошади. Случай произошел в США, в штате Мичиган на окраине города Дирборн, в 1872 году. Встав на землю после падения, Генри поставил в своей жизни цель, создать такой вид транспорта для людей, который был бы безопасным, удобным в отличие от повозок (карет) с лошадьми или просто езды сидя верхом на седле.
Ford Motor Company.
Повзрослев Генри Форд, объединился в команду со своими 11 друзьями, такими же энтузиастами, как и он сам. 16 июня 1903 года они все вместе собрали стартовый капитал в сумму 28000 долларов и подали заявление на создание в штате Мичиган производственного предприятия.
Так появилась компания Ford Motor Company. Первым её автомобильным изобретением была «бензиновая коляска», которая получила марку «Модель А» и имела привод от двигателя в восемь лошадиных сил.
Спустя 10 лет после первого выпуска автомобиля, Генри Форда во всем мире прозвали гением, подарившим всему земному обществу первый доступный для каждого человека автомобиль — Ford T. Помимо этого Ford Motor Company – самая первая компания в мире, которая ввела конвейерное производство автомобилей. Вследствие технического прогресса и постоянному введению инноваций, Форду удалось снизить цену на модель Tin Lizzy с 850 до 290 долларов.
Так в чем же секрет успеха автомобильного производства Ford Motor Company, которое длится вот уже свыше ста лет? Генри Форд создавая свою компанию, мечтал изобрести такой автомобиль, цена которого в сумме составляла бы годовой оклад простого рабочего, трудившегося на заводе по сборке машин в Детройте.
Ford Model A
Самый первый автомобиль Генри Форда — «Модель А».
Компания Ford за всю свою историю, которой уже где-то 140 лет выдержала и подверглась большим переменам. Но, не смотря на это, самые главные принципы работы производства остались неизменными — автомобили для людей должны быть доступные, современные и надёжные.
Генри Форд родился 30 июля 1863 года в поселке Спрингфилд штата Мичиган. Его родителей звали Уильям и Мэри Форд (William and Mary Ford), у которых было шестеро детей. Генри был самым старшим из них. Отец с матерью владели фермерским хозяйством, дела которого процветали. Поэтому все детство будущего гения прошло на семейной ферме, где Генри ходил в обычную сельскую школу, а после неё помогал родителям по хозяйству.
Когда Генри исполнилось 12 лет, он соорудил для себя небольшую мастерскую, в которой проводил всё свободное время с большим удовольствием. Спустя несколько лет он создаст свой первый паровой двигатель, сконструированный в этой мастерской.
Самый знаменитый и популярный автомобиль прошлого века — Ford T. Именно благодаря серии этой марки, автомобиль превратился из игрушки для богачей в средство для передвижения, которое доступно каждому человеку.
Генри Форд устраивается на работу помощником машиниста, перебравшись в Детройт в 1879 году. Спустя три года переезжает в Дирборн, где около пяти лет конструирует и ремонтирует паровые двигатели, но иногда подрабатывая на заводе в Детройде. Через 9 лет Форд женится на Кларе Брайент и в 1888 году на лесопильном заводе успешно занимает одну из руководящих должностей.
Через три года в 1891 Форд становится инженером в компании Edison Illuminating, а спустя ещё два года его повысят до должности главного инженера. Теперь у Форда появляется больше свободного времени плюс весьма достойный заработок. Благодаря этому Генри смог больше уделять времени созданию двигателя внутреннего сгорания.
Первый вариант двигателя разрабатывался на кухне, в доме самого Форда. После этого он скрепил его с четырёхколёсной велосипедной рамой. В результате получился квадроцикл. В 1896 году именно он стал первым автомобилем марки Форд.
В 1899 году Генри Форд уходит из Edison Illuminating, чтобы основать собственную компанию Detroit Automobile. Год спустя фирма обанкротится, но, несмотря на это Форд успеет произвести несколько моделей гоночных машин. Также в октябре 1901 года Форд поучаствует в автогонках, где станет победителем, обогнав тогда нынешнего чемпиона США Александра Уинтона (Alexander Winton).
Модель Т выпускалась в виде кабриолета, пикапа, легковой машины и других типов моделей.
Ford Motor образовался в 1903 году. Генри Форд основал предприятие вместе с 12 учредителями из штата Мичиган. Сам Форд был во главе компании, занимая должность вице-президента и главного инженера, а также ему принадлежал контрольный пакет акций 25 процентов.
Чтобы создать завод автомобильного производства, компания выкупила фургонную фабрику Мэк Авеню в Детройте и переделала её под свое направление деятельности. Форд нанимал по свое руководство бригады рабочих из 2-3 человек и они изготавливали автозапчасти на заказ.
23 июля 1903 года был продан первый автомобиль Форда. Первая модель была «бензиновая коляска» или Model А с приводом от двигателя мощностью в восемь лошадиных сил. На рынке автомобиль был приставлен как простая и доступная машина, на которой за рулем может сидеть даже подросток в 15 лет. После этого Генри Форд стал основным владельцем и главным президентом Ford Motor.
Благодаря первым представителям компании Шрайберу, Торнтону, Перри (Schreiber, Thornton, Perry) из Великобритании в 1907 году был придуман логотип Ford в виде овала. Он характеризовал автомобили Ford, как символ надежности, экономичности и олицетворял «клеймо высшей пробы».
Генри Форд руководил общей работой производства. В течение следующих пяти лет под его управлением было задействовано девятнадцать букв от Model А до Model S, часть из которых так и осталась на начальном или исследовательском уровнях и не дошли до уровня производства и выпуска на рынок.
Генри Форд смог исполнить свою мечту только в 1908 году. Он выпустил модель Tin Lizzy (Жестяная Лиззи, так её ласково называли американцы) — Model T. Эта автомодель стала самой известной за всю историю автоиндустрии.
Базовая цена машины получилась 260 долларов. В течение первого года выпуска было продано одиннадцать тысяч автомобилей Model T. Её появление на рынке означало как новая эра или эволюция вида транспорта.
Фордовские автомобили не требовали сложного технического обслуживания, они могли проехать даже по неровным сельским дорогам, в общем, они были просты в управлении. Вследствие этого спрос на автомобиль постоянно рос, и он стал объектом массового производства.
Также на основной базе строения Model Т производятся машины других модификаций: микроавтобусы, скорая помощь, мелко грузовой транспорт, небольшие фургоны и т.д. Помимо этого изготавливалась версия и для военной скорой помощи.
С повышением производительности труда и качества продукции, рос и потребительский спрос у покупателей. Генри Форд становится самым первым в мире, кто решил внедрить в автомобильное производство конвейер. Благодаря ему рабочий, оставаясь на одном месте, выполнял всего одну операцию, поэтому каждые десять секунд с конвейера спускалась абсолютно новая Model Т. Конвейерное производство стало одним из значимых этапов в революции производства.
Семейная компания.
Генри Форд вместе со своим сыном Эдселем (Adsel Ford) В 1919 году выкупили акции компании Ford Motor у других учредителей предприятия за 105 568 858 долларов, после чего компания стала их семейной фирмой, а Форды её единственными владельцами. Вдобавок Эдсел Форд получил в наследство от отца должность главного президента Ford Motor и занимал этот пост, пока внезапно не скончался в 1943 году. В дальнейшем после смерти сына Генри Форду приходится вновь возглавить управление компанией.
Ford Fordor Deluxe
Ford Fordor Deluxe — также в своё время стал дико популярной автомоделью.
В 1927 году Model A стала первой, на которой логотип Ford был изображен на решётке радиатора в виде овального силуэта. Большинство автомобилей Ford до конца пятидесятых годов были выпущены с тёмно-синим значком логотипа, который и сейчас известен многим покупателем. Но, не смотря на то, что овальный образец был утверждён в качестве официального логотипа компании, его не наносили на машины до середины семидесятых годов.
Постоянный прогресс и ускоренный стиль жизни человека, заставлял компанию внедрять нововведения технологий и усиление мощностей. Ford Motor Company всегда старалась идти в ногу со временем.
В 1932 году компания представила публике V-образный 8-цилиндровый двигатель. Первого апреля того же года фирма Ford стала первой, кто выпустил подобный монолитный двигатель. Серия автомобилей с этим двигателем стала самой популярной у большинства американцев.
Ford Fairlane
Есть предположение, что наша «Чайка» — это копия Ford Fairlane. А как думаете вы?
В этом же году Ford – стала самой распространённой машиной, из-за её ремонтопригодности и доступным в магазинах США автозапчастям. В 1934 году – были выпущены грузовые автомобили Ford (с полностью доработанным двигателем) для крупных городов и рабочих ферм.
После, с каждым годом популярности личного транспорта у людей появляется и проблема безопасности в машинах. Форд не проходит стороной эту проблему. Он опять становится тем, кто самый первый начинает применять в производстве автомобиля безопасные стёкла. Главным принципом общей политики компании была и остаётся забота о человеческой жизни. Поэтому на заводе постоянно велись разработки по снижению риска для человека, находившегося за рулем. Покупатели всегда щедро платили за это своей любовью и предрасположению именно к марке Ford.
Марка Ford становится знаменитой и популярной не только в Америке. Помимо неё Ford Motor Company открывает во всем мире большую сеть заводов, магазинов и филиалов, туда также попадает Россия и Европа. Во всем мире фордовские автомобили имеют хорошие продажи и становятся народной маркой подлинного качества.
50-60-е годы.
После второй отечественной войны Генри Форд в 1945 году передает по наследству свои полномочия главы компании Генри Форду второму (старший внук). Помимо этого Генри Форду старшему в мае 1946 года была вручена почетная премия за заслуги в области автопроизводства, а также золотая медаль в конце этого же года за заслуги перед обществом Американским институтом нефти (American Petroleum Institute).
Ford F-100
Ford F-100 – стал культовой машиной среди пикапов, подсадив на него огромное количество жителей США. Эта модель популярна до сих пор.
7 апреля 1947 года, в городе Дирборн, в возрасте 83 лет умер Генри Форд старший. Его смерть стала завершением начального и бурного периода компании Ford Motor и, несмотря на это, открыла дверь в новую автомобильную эпоху.
Внук Генри Форда старшего достойно продолжает работу и мечту своего деда. Появляется, нова модель Ford. 8 июня 1948 года на автомобильной выставке в Нью-Йорке торжественно представлена модель будущего 1949 года. Её уникальный дизайн выделял модель среди всех остальных: независимая передняя подвеска, открывались задние боковые стёкла, а также боковые панели в гладкой форме.
Новинка в автомобильном дизайне – стала объединением кузова и крыльев. Ford Motor Company достигает высокого объема продаж этих моделей в 1949 году, что превышает показатели по продажам с 1929 года. Прибыли компании начинают расти с высокой скоростью, а это в свою очередь позволяет увеличить количество заводов, филиалов и открыть новые инженерно-исследовательские центры.
Модель Ford Thunderbird – в тех годах становится самым шикарным и легендарным спортивным автомобилем
В дальнейшем развитии компании открываются новые направления её деятельности: 1. Ford Motor Company – сам финансовый бизнес марки FORD. 2. American Road Insurance Company – страховая компания. 3. Ford Parts and Service Division — автоматизированная замена запчастей. А также производство автомобильной электроники и техники, космические технологии, разработка компьютеров и т.д.
И, в конце концов, Ford Motor Company в январе 1956 года становится ОАО (открытое акционерное общество). Сейчас, на данный момент времени насчитывается свыше семисот тысяч учредителей и обладателей акций.
В шестидесятые годы в центр внимания фирмы попадает молодое поколение. Форд младший перенаправляет производство автомобилей на выпуск спортивных и недорогих машин предназначенных для молодёжи.
После этого, в 1964 году, на рынке впервые появляется модель Ford Mustang, названная в честь военного самолёта P-51. Её особенностью было, то, что использовался новый вид двигателя. В нем совмещались трансмиссия и ведущий мост вместе. Также отличия были в новом дизайне кузова, который сочетал в себе все современные направления тех годов.
Ford Mustang
Ford Mustang — стал настоящим шедевром среди спортивных автомобилей и молодого поколения.
Подобного интереса к марке Ford, не наблюдалось с тех пор как выпустили первую Model A. Ожидания компании превзошли себя. Было продано около ста тысяч автомобилей Mustang в первые три месяца после запуска продаж.
После такого успеха воодушевленные сотрудники компании, продолжают работать над совершенствованием дизайна. Начинают применяться все новые тенденции и инновации автомобильного дизайна. В результате чего на свет появляются модели Corina и Transit.
В свою очередь Ford Motor Company продолжает работать над проектами по безопасности езды на дорогах. Доказывая тем самым, что прибыль не главная цель компании.
Ford GT40
Model GT40 выигрывает в Ле-Мане двадцати четырёх часовую гонку, тем самым оборвав первенство Ferrari, в данных соревнованиях.
Также Ford Motor Company в 1970 году первая в мире компания, внедрившая дисковые тормоза в широкое производство.
В 1976 году и в дальнейшем официальный овальной формы логотип Ford с синим фоном и серебристыми буквами, появляется на всех кузовах автомобилей. Это позволило узнавать машины Ford в любой стране мира.
Model Ford Taurus
Model Ford Taurus – была удостоена награды «автомобиль года» в США, из-за своей комфортности и экономичности, ставшая также популярным хитом.
После, в свою очередь появились такие модели как сам Ford Taurus и Mercury Sebale. Они были придуманы как автомобили с экономией топлива. Дизайнеры и специалисты компании постоянно внедряли инновации, чтобы создать действительно необходимую машину для людей с уровнем дохода среднего класса.
Стоит отметить, что Model Ford Taurus разрабатывалась как автомобиль, в котором каждая его деталь была изготовлена до совершенства. Такая плодотворная работа принесла компании успех и в 1986 году Ford Taurus стал машиной номер один в Америке и был признан лучшим автомобилем того же года.
После этих событий был выпущен Model Ford Mondeo. Он заменил Model Ford Scorpio, несмотря на то, что уступал ему в размерах в начале производства.
Потом в 1994 году появился целый ряд новинок помимо таких как Model Ford Mondeo. Это новый микроавтобус Windstar, видоизменённая Model Ford Mustang, а также новинка Model Ford Espire.
Спустя немного времени в Северной Америке появились новые улучшенные модели Model Ford Taurus и Model Mercury Tracer. В них были выполнены первые, видоизменяя дизайна кузова и салона после устаревшей стилистики восьмидесятых годов. Также в Европейских странах, публике были показаны изменения дизайна минивэна Galaxy, Model Ford Fiesta и пикапа F-серии.
Новый минивэн Model Ford Galaxy был сконструирован на той же платформе, что и Ford Seat Alkhambra и Ford Volkswagen Sharan, их внутренние и внешние отличия можно было легко пересчитать по пальцам.
Настоящее время.
Спустя много лет главным принципом производства Ford Motor Company стало сочетание вместе совершенствование автомобилей плюс минимальный затраты на производство, что позволяет компании выпускать автомобили мирового уровня.
Сейчас компания Ford выпускает на продажу во всем мире свыше семидесяти модификаций автомобилей под разными марками Ford, Lincoln, Aston Martin, Mercury и т.д. Также Ford Motor Company имеет долю акций в других компаниях, таких как Kia Motors Corporation или Mazda Motor Corporation.
Model Ford Focus – новая модель, которая сменила конвейерное производство Model Ford Escort. Ford Focus приобрел бешеную популярность у российских граждан ещё до запуска основного производства. Купить двигатель на Форд Фокус 2 можно по этой ссылке.
Новый официальный завод Ford Motor Company был открыт 9 июля 2002 года в городе Всеволжск в Ленинградской области Российской Федерации. В российском филиале компании происходит полный процесс кругооборота производства.
В 1903 году, найдя одиннадцать единомышленников и собрав в качестве уставного фонда 28000 долларов, Генри Форд основал автомобилестроительную фирму, «Форд Мотор Компани», но сама история Форд началась гораздо раньше….
История Форд
Генри Форд — им созданы: первая машина, первая противоугонная система и первый водитель в Америке!
В 1893 после нескольких лет экспериментов Генри Форд построил свой первый автомобиль, который тогда скорее напоминал ящик на колесах, приводимый в движение самодельным бензиновым двигателем. Первый автомобиль Форд издавал много шума и пугал не только людей, но и лошадей — основной вид транспорта. Это вошло в историю Форд и в жизнь Детройта.
Когда Форд оставлял машину на улице, без присмотра, то сразу же находились желающие на ней покататься, так что в конце концов Генри Форд стал носить с собой цепь, на которую привязывал свое изобретение к фонарному столбу. Выходит что и первое противоугонное устройство придумал тоже Форд.
Генри Форд первый водитель в Америке
Городские власти обязали будущего Форда получить специальное разрешение на управление самодвижущимся экипажем. Таким образом, Генри Форд официально стал первым водителем Америки!
Продав в 1896 году за 200 долларов свой первый автомобиль Чарльзу Эйнсли, Генри Форд в сарае за домом в котором он жил, построил свой второй автомобиль. Новый автомобиль получил название «Квадроцикл» за то, что имел двигатель мощностью в четыре лошадиные силы, имел раму от детской коляски и четыре велосипедных колеса.
Форд задумался о массовом производстве автомобилей и нашел нескольких энтузиастов.
Генри Форд и Детройтская автомобильная компания
В 1899 году они создали «Детройтскую автомобильную компанию» (переименованную затем в «Компанию Генри Форда»). Производство Форда началось на небольшой фабрике, специализирующийся на выпуске карет.
В период с 1899 по 1902 год Детройтская Автомобильная Компания выпустила двадцать пять автомобилей. Далее Форд сделал то, чего в дальнейшем никогда не позволял себе автомобильный король: он самолично, в качестве гонщика, выступил на состязаниях. Форд вызвал на состязание гоночного чемпиона Америки Александра Уинтона из Кливленда, известного строителя «уинтоновского» автомобиля. Для этих гонок Форд сконструировал специальный двухцилиндровый мотор более компактного типа. Встреча Форда с Уинтоном произошла в Детройте на ипподроме Гринд-Пойн. Победителем на гонках остался Форд, пришедший к финишу значительно раньше своего соперника. Автомобили Форда установили рекорд скорости, сделав фамилию Форд известной по всей Америке!
В 1902 году Генри Форд вышел из состава учредителей предприятия, которое затем было преобразовано в фирму «Кадиллак», ставшую в 1909 году подразделением «Дженерал моторс».
История создания компании «Форд Мотор Компани»
В 1903 году, найдя инвесторов и собрав в качестве уставного фонда 28000 долларов, Генри Форд основал автомобилестроительную фирму, компанию «Форд Мотор Компани». Акционерное общество Форда владело 1 000 акций Ford Motor Company. В собственности Форда было 255 акций.
На разработку Model A были потрачены все средства новосозданной компании, но модель оказалась очень успешной – за полтора года выпуска было продано 1708 экземпляров, обеспечив Ford Motor Company безоблачное будущее. Стоит заметить, что уже в этой машине Генри Форд сформулировал свое видение оптимального автомобиля: разумная конструкция, небольшая масса и умеренная цена.
Компания сразу же начала приносить прибыль — 1 октября 1903 они получили 37 000 долларов прибыли.
В 1904 году было основано представительство Форд в Канаде. В 1907 году открыто представительство марки Форд в России, которое функционировало до 1917 года.
Первые серийные автомобили компании Форд
Первые автомобили выпущенные на заводе Форда были — Ford A, Ford B, Ford К и Ford S.
Ford A
Автомобиль Ford A одно из первых существенных достижений Генри Форда — коляска для перевозки пассажиров. Её работа производилась за счёт бензинового двигателя, мощность которого составляла восемь лошадиных сил. Двигатель располагался под сидениями пассажиров.
Ford C
Автомобиль Ford Model C выпускался в 1905 году и представлял собой вариант первого Ford Model A с более современным видом, немного более мощным двигателем и на 15 см большей колесной базой. имел двухцилиндровый двигатель мощностью 120,5 кубических дюймов, который развивал 10 лошадиных сил, карбюратор Холли, 2-скоростная планетарная трансмиссия с реверсом, конусная муфта, цепной привод, 28-дюймовые деревянные спицевые колеса и 78-дюймовая колесная база. Цена в версии с 2 пассажира — 800,00 долларов в версии 4 пассажира — 950,00 долларов. На базе C был создан первый грузовик. Ford Model C была заменена Model F в 1905 году.
Обе модели автомобилей A и C были выпущены в один тот же момент, в модели A устанавливались двигатели модели С, такой вариант назывался Ford Model АС. На Model C в первое время ставился двигатель Flat-2 (8 л.с.), а затем в 1905 году он стал 10-сильным (7 кВт), и располагался под сидением, как и на Model A.
Ford B
Автомобиль Ford B это первый автомобиль фирмы с переднемоторной компоновкой и карданным валом. В сравнений с моделью А модель B имела более низкий центр тяжести, что улучшило управляемость. Двигатель рядный, четырехцилиндровый, мощностью в 24 л.с. Рядная четверка на долгие годы станет визитной карточкой автомобилей Ford. Считался престижным, туристическим автомобилем. Стоил — 2000 долларов. Было выпущено — 500 штук. Выпускался Ford B с 1904 по 1906 год.
Ford F
Автомобиль Ford F была дальнейшая разработка Ford A и Ford B, автомобиль стал более крупным, современным и более роскошным. Ford Model F имел мотор 127 кубических дюймов, два цилиндра, против которых развивались 16 лошадиных сил, карбюратор Холли, 2 скорости вперед и назад планетарная передача, цепной привод, дифференциальные тормозные системы, 30-дюймовые деревянные спицевые колеса и 84-дюймовая колесная база.
Это был четырёхместный фаэтон, производство которого началось в 1905 году и закончилось в 1906. Цена купе — 2 двери 4 пассажира Touring Car $ 1,000,00 и $ 1,200.00 для 2-дверного 2 пассажирского купе. В 1906 Ford F сменили модели Ford K и N.
Ford K
Автомобиль Форд К, выпущенный в 1906 году, стал первым автомобилем Ford Motor с шести цилиндровым двигателем мощностью 40 л.с. и был известен как «роадстер джентльмена». Машина получилась дорогой и не пользовалась спросом. Ford K продавался по цене 2 800 долларов.
Ford N
Ford N Был представлен в 1906 году в качестве преемника для моделей A, C и F, как линейка недорогих автомобилей компании. Форд Н отличается от своих предшественников тем, что имеет переднее расположение рядного 4-цилиндрового двигателя, мощностью 15 л.с., передававшего энергию на задние колеса через длинный вал. В целом эти модель получилась успешной, пользовалась популярностью из-за доступной цены (500 долларов) и хорошо продавалась.Выпуск Ford N позволил компании Ford Moto Company немного поправить свои дела и восстановить былую славу производителя дешевых и надежных автомобилей, слегка пошатнувшуюся после выпуска неудачной модели K. За два года было выпущено 7000 автомобилей этой модификации. В 1908 году выпуск Model N был прекращен.
Легендарный автомобиль Ford T
В 1908 год Форд решается на рискованный шаг: отказывается от всего модельного ряда и начинает производство новой разработки, модели «T». Это был принципиально новый автомобиль который изменил мир.
Подробнее о легендарной модели Ford T читайте здесь.
В 1919 году Генри Форд выкупили акции предприятия у других акционеров за 105 568 858 долларов США и стал единственным владельцем компании.
К 1920 году половина всех автомобилей в США были Model T. Повсеместно на автомобилестроительных предприятиях стал внедряться конвейер.
В конце 20-х компания Ford Motor начала уступать свою долю рынка GM и Chrysler, тогда в 1922 году Форд расширил свое влияние в сегменте роскошных автомобилей благодаря приобретению Lincoln Motor Company.
Сравнительно удачной была линия автомобилей Ford Mercury «Меркюри», запущенная в 1938.
В конце 1938 году было создано подразделение Mercury и стало занимать среднюю ценовую нишу между марками Ford и Linkoln.
Ford непосредственный участник второй мировой войны
В период военных действий заводом «Форд» было выпущено 57 тысяч двигателей для самолётов, 86 тысяч бомбардировщиков «B-24 Либерейтор» и 250 тысяч танков. Для США во Вторую мировую войну компания выпускала армейские грузовики и внедорожники и танки для американских войск на предприятиях Ford GPW и Willys MB.
Ford построил на территории нацистской Германии производство, которое выпустило для нужд Вермахта 12 тыс. гусеничной и 48 тыс. единиц колёсной техники.
Генри Форд умер в возрасте 83 лет 7 апреля 1947 года но это не стало концом истории Форд, компания Ford Motor продолжала активно развиваться.
В 1955 году представлен культовый Thunderbdir, известный также как T-Bird.
Модель выпускалась в одиннадцати поколениях с незначительными перерывами до 2005 года. Всего было произведено 4,4 миллиона автомобилей Thunderbird.
В 1964 году появляется легендарный «Мустанг». Его ведущая особенность — сочетание в новом двигателе двух агрегатов: ведущего моста и трансмиссии. Внешний вид сочетал в себе все лучшие тенденции дизайна пятидесятых — шестидесятых годов.
Форд» выпускает две модели: «Меркури-Сейбл», «Форд-Таунус». Все детали в автомобилях абсолютно совершенны. В результате «Таунус» стал автомобилем 1986 года.
В 1986 году была приобретена английская марка Aston Martin. Во II квартале 2007 года Ford Motor Company продала подразделение Aston Martin консорциуму инвесторов за $925 млн.
В 1990 году приобретенную Jaguar за 2,5 миллиарда и в 2000 Land Rover за 2,73 миллиарда долларов отошли к индийской Tata Motors в 2008. Оба бренда обошлись в 2,3 миллиарда долларов.
В 1999 году приобретенный Volvo Cars был продан 29 марта 2010 года китайская компания Zhejiang Geely объявила о достижении договорённости о приобретении Volvo Cars у компании Ford Motor за 1,8 млрд долларов. Все интеллектуальные права на разработки шведской компании, как планируется, останутся у Volvo, а Geely получит к ним полный доступ. Сделка была закрыта в начале августа 2010 года.
Также Ford Motor Company имеет долю акций в других компаниях, таких как Kia Motors Corporation и Mazda Motor Corporation.
Руководство Ford
Компания Ford Motor уже на протяжении более чем 100 лет контролируется семьёй Фордов, являясь, таким образом, одной из наиболее крупных компаний, находящихся под семейным контролем, в мире. В то же время, Ford Motor Company является публичной компанией, акции которой котируются на Нью-Йоркской фондовой бирже. Семье Форд на октябрь 2010 года принадлежало 40 % голосующих акций Ford, остальные находились в свободном обращении.
Председатель совета директоров — Вильям Форд мл. (William Clay Ford, Jr). Президент — Алан Малалли.
Показатели деятельности Ford
В 2009 году компанией (вместе с контролируемыми марками) было произведено 4,8 млн машин (годом ранее — 5,5 млн), в том числе Ford Europe — 1,6 млн, Volvo Cars (ныне не принадлежащая Ford) — 0,32 млн. Сейчас «Форд» выпускает более семидесяти моделей автомобилей. Среди них самые известные: «Линкольн», «Форд», «Ягуар», «Астон-Мартин». Компания «Форд», имеет значительное количество акций Киа Моторс Корпорейшн и Мазда Мотор Корпорейшн.
Общее количество занятых в компании — 178 тыс. человек (2010 год), годом ранее — 198 тыс. человек. Выручка компании в 2009 году составила $118,31 млрд (в 2008 году — $145,11 млрд), чистая прибыль — $2,72 млрд (в 2008 году чистый убыток $14,77 млрд).
Ford в Europe
Ford of Europe имеет штаб-квартиру в Кёльне, (Германия); президент и генеральный директор — Джим Фарли. Объём отгрузок Ford of Europe в 2010 году составил 1,57 млн автомобилей; выручка Ford of Europe по US GAAP в 2010 году составила $29,5 млрд, прибыль до налогообложения — $326 млн.
Европейский центр исследований и инноваций Ford разработал систему освещения, которая может идентифицировать пешеходов, велосипедистов или крупных животных в темное время суток. Благодаря поворотным фарам, установленным в бампере автомобиля, пешеходы, которых распознает бортовая система, подсвечиваются. Merkur — автомобильная марка, принадлежит Кёльнскому отделению Ford (Германия). Как правило эти автомобили поставлялись на Американский континент со своей эмблемой Merkur. Модели всего две — Sierra (в большинстве своём-XR4TI) и Scorpio.
Отличие от европейских значительны. Касалось не только оптики, бамперов, обвеса, круиза-контроля, кондиционера, коробки-автомат (механика — опция), дисковых тормозов, но и пассивной безопасности кузова и его жесткости, что привело к увеличению веса данных моделей по сравнению с более «простыми» европейскими комплектациями.
Ставились и более мощные моторы, с турбо, как на модели XR-4Ti 2.3L (170 л.с.).
Автобусы Ford, с двигателями, работающими на альтернативном топливе
Ford модифицировал 6,8 литровый двигатель внутреннего сгорания Triton V-10 автобуса Е-450 для работы с водородом в 2004 году. Мощность двигателя 235 л.с.
Двигатели внутреннего сгорания, модифицированные для работы на водороде называются на английском языке hydrogen in an internal combustion engine (H2ICE).
Баки для хранения водорода поставляет канадская компания Dynetek. В баках хранится газообразный водород под давлением 350 бар, эквивалентный 30 галлонам бензина. Дальность пробега на одной заправке 240 км. Автобус перевозит 12 пассажиров.
К августу 2008 года двадцать водородных Е-450 эксплуатируются в Северной Америке.
Компания Ford стала одним из немногих производителей, доживших до наших дней. А ведь в период с 1903 по 1908 год только в США было зарегистрировано около 240 автомобильных марок, но далеко не в каждой нашелся непоседа сродни Генри Форду.
В настоящее время Форд — третий на рынке США после GM и Toyota, и второй в Европе после Volkswagen .Форд и сейчас в производстве и не капли не устаревая продвигается на автомобильном рынке.
Модельный ряд автомобилей Ford
- 1908-1927 Ford Model T
- 1928 Ford A
- 1938 Ford Mercury
- 1955-2005 Ford Thunderbdir
- 1964 Ford Mustang Convertible
- 1964 Ford Mustang GT-350
- 1965-1967 Ford GT40 II
- 1965-2011 Ford Transit
- 1965-1973 Ford F-100 Pickap
- 1968-1976 Ford Escotr I
- 1969-1974 Ford Capri I
- 1969-1971 Ford Falcon XW
- 1970-1974 Ford Falcon XY
- 1970-1982 Taunus
- 1972-1979 Ford Falcon XB
- 1972-1976 Ford Consul Coupe GGCL
- 1972-1985 Ford Granada
- 1974-1980 Ford Escort II
- 1974-1977 Ford Capri II
- 1975 Ford Mustang Boss 302
- 1976-1983 Ford Fiesta I
- 1976-1969 Ford Falcon
- 1977-1982 Ford Bronco I F150
- 1978-1987 Ford Capri III
- 1979-1988 Ford Falcon XF
- 1980-1985 Ford Escort III
- 1982-1993 Sierra
- 1983-1989 Ford Fiesta II
- 1983-1991 Ford Bronco II
- 1983-2005 Ford Thunderbird
- 1983-1986 Ford Orion I
- 1985-1990 Ford Orion II
- 1985-1994 Scorpio I
- 1986-1991 Ford Taurus MkI
- 1986-1997 Ford Aerostar
- 1986-1990 Ford Escort IV
- 1986-1992 Econovan Kasten KAA
- 1987-1995 Ford Tempo
- 1988-1992 Ford Probe I
- 1989-1995 Ford Fiesta III
- 1989-1993 Ford Falcon EA
- 1990-1992 Ford Escort V
- 1990-1993 Ford Orion III
- 1991-1993 Ford Falcon EB
- 1991-2011 Crown Victoria
- 1991-1995 Ford Taurus MkII
- 1992-2007 Econoline E-150
- 1992-1996 Ford Bronco III EFI
- 1992-1995 Ford Escort VI
- 1993-1998 Ford Probe II
- 1993-2006 Ford Maverick
- 1993-1997 Ford Aspire
- 1993-1996 Mondeo I
- 1994-1998 Scorpio II
- 1994-2003 Explorer Sport
- 1994-1997 Ford Falcon EF
- 1995-2004 Ford Freda
- 1995-2002 Ford Fiesta IV
- 1995-1999 Ford Escort VII
- 1995-1999 Ford Escort VII Express AVL 95
- 1995-2001 Ford Contour
- 1995-2005 Ford Windstar
- 1995-2006 Galaxy
- 1996-2000 Ford Taurus MkIII
- 1996-2001 Mondeo II
- 1996-2002 Ford Expedition
- 1996 Ford Ka
- 1997-2003 Ford F-150 Regular Cab
- 1997-2002 Ford Puma
- 1998-2004 Ford Ranger
- 1998-2004 Ford Focus
- 1998-2002 Ford Falcon RX6
- 1998-2002 Ford Explorer I
- 1998-2991 Cougar
- 1998-2012 Courier
- 2000-2005 Ford Excursion
- 2000-2007 Ford Ikon
- 2000-2007 Ford Taurus MkIV
- 2000-2004 Ford F-250 Crew Cab
- 2001-2012 Ford F-650 Super Crew Cab
- 2001-2007 Mondeo III
- 2001-2007 Ford Escape
- 2002-2008 Ford Fiesta V
- 2002-2006 Ford Expedition II
- 2002 -2005 Ford Explorer II
- 2003-2003 Model U
- 2003-2009 Ford Tourneo
- 2003-2012 Ford Falcon RX8
- 2003-2008 Ford F-150 Super Cab Small
- 2003 Ford Focus C-Max
- 2003-2006 Ford Freestar
- 2003-2012 Ford Fusion2004-2011 Ford Focus II
- 2003-2003 Ford 427
- 2003-2006 Street Ka
- 2003-2007 Ford Fairlane
- 2004-2006 Ford Ranger II
- 2004-2010 Ford F-250 Super Cab Super Duty Long
- 2004-2010 Ford F-350 Regular Cab Super Duty
- 2004-2009 Ford GT 500 IV2011 Ford Focus III
- 2004-2007 Ford Five Hundred
- 2005-2010 Ford Explorer III
- 2005-2007 Ford Freestyle
- 2006-2010 Ford F-450 Super Duty
- 2006 Ford S-Max
- 2006 Ford Galaxy II
- 2006 Ford Edge
- 2007-2009 Ford Taurus MkV
- 2007-2011 Ford Ranger Rap III
- 2007-2012 Ford Escape Hybrid
- 2007 Ford Expedition III MAX
- 2007 Mondeo IV
- 2008 Ford Taurus X MkV
- 2008 Ford Kuga
- 2008 Ford Flex
- 2008 Ford Fiesta VI
- 2008 Ford F 150
- 2010 Ford Taurus MkVI
- 2011 Ford Explorer IV
- 2012 Ford B-Max
Компания выпускает широкий спектр легковых и коммерческих автомобилей под марками «Форд». Компания разделена на три структуры по географическому признаку: Ford North America, Ford Asia Pacific и Ford of Europe. Ранее каждое из этих подразделений имело собственный модельный ряд, но в 2006 году руководитель компании Малалли объявил о новой стратегии «Единый Ford», согласно которой Ford должен постепенно начать выпускать глобальные автомобили, общие для всех рынков, и первым из них стал Ford Focus III. Предприятия Ford (на 2010 год — всего 80) расположены в США, РФ, Канаде, Мексике, Бразилии, Аргентине, Испании, Китае и прочих странах.
| Ford Motor Company | |
 |
|
| Тип |
Публичная компания |
|---|---|
| Листинг на бирже |
NYSE: F |
| Девиз компании |
Feel the difference. |
| Год основания |
1903 |
| Расположение |
|
| Ключевые фигуры |
Вильям Форд мл. (председатель совета директоров) |
| Отрасль |
Автомобилестроение |
| Продукция |
Легковые и коммерческие автомобили: |
| Оборот |
▲ $173,9 млрд[1] (2007 год) |
| Чистая прибыль |
▲ -$2,7 млрд[1] (2007 год, чистый убыток) |
| Число сотрудников |
▼ 245 тыс. человек[1] (2007 год) |
| Веб-сайт |
www.ford.ru |
Ford Motor Company (Форд Мо́тор Ка́мпэни) (NYSE: F) — североамериканская автомобилестроительная компания, производитель автомобилей под марками «Ford», «Mercury», «Lincoln», а также владелец марки «Mazda».
Четвёртый в мире производитель автомобилей по объёму выпуска за весь период существования; в настоящее время — третий на рынке США после GM и Toyota, и второй в Европе после Volkswagen.
Занимает 7 место в списке крупнейших публичных компаний США Fortune 1000 по состоянию на 2009 год[2] и 19 место в списке крупнейших мировых корпораций Fortune Global 500 2009 года[3] (2009 год).
Штаб-квартира кампании располагается в городе Дирборн (пригород Детройта, штат Мичиган), а её европейского филиала — в Кёльне, ФРГ.
Содержание
- 1 История
- 1.1 Слияния, поглощения и продажи
- 2 Собственники и руководство
- 3 Деятельность
- 3.1 Модельный ряд
- 3.2 Концепт кары
- 3.3 Показатели деятельности
- 3.4 Ford в России
- 3.4.1 История работы Ford в России
- 3.4.2 Современное положение
- 3.4.3 Российское производство Ford
- 4 Спорт
- 4.1 Ралли
- 4.2 Формула-Форд
- 4.3 Формула-1
- 5 Критика
- 6 См. также
- 7 Примечания
- 8 Ссылки
История
Компания основана в 1903 году Генри Фордом, который создал её, получив на развитие бизнеса $28 000 от пяти инвесторов. Компания Ford получила известность как первая в мире применившая классический автосборочный конвейер.
Генри Форд в 1914 году
Первой получившей массовое признание моделью, выпускаемой компанией, стал Ford Model T, выпускавшийся в 1908—1926 годах.
В конце 1920-х годов с компанией руководством СССР был заключён договор о помощи при строительстве автозавода в Нижнем Новгороде. Ряд легковых и грузовых машин компании «Форд» того времени послужил прототипами для первых серийных образцов нового советского автозавода ГАЗ-А и ГАЗ-АА.
В конце 1930-х годов компания не пользовалась доверием американских военных из-за нескрываемых пронацистских симпатий основателя[4][5][6]. Тем не менее, со вступлением США во Вторую мировую войну компания начала выпуск армейских грузовиков и джипов (уже не своей конструкции — Ford GPW был адаптированной версией Wyllis MB), выступала смежником в танкостроительной программе США.
Слияния, поглощения и продажи
Во II квартале 2007 года Ford Motor Company продала подразделение Aston Martin консорциуму инвесторов за $925 млн[7].
29 марта 2010 года китайская компания Zhejiang Geely объявила о достижении договорённости о приобретении Volvo Cars у компании Ford Motor за 1,8 млрд долларов. Официальный представитель Volvo Пер Ааке Фреберг подтвердил информацию о состоявшейся продаже шведского бренда. Как ожидается, сделка должна быть закрыта в течение нескольких недель. Все интеллектуальные права на разработки шведской компании, как планируется, останутся у Volvo, а Geely получит к ним полный доступ.[8]
Собственники и руководство
Компания Ford Motor уже на протяжении более чем 100 лет контролируется семьёй Фордов, являясь, таким образом, одной из наиболее крупных компаний, находящихся под семейным контролем, в мире. В то же время, Ford Motor Company является публичной компанией, акции которой котируются на Нью-Йоркской фондовой бирже. Семье Форд на февраль 2008 года принадлежало 40 % голосующих акций Ford, остальные находились в свободном обращении.[9]
Председатель совета директоров — Вильям Форд мл. (William Clay Ford, Jr). Президент — Алан Малалли.
Деятельность
Ford model B (1932) — первый в мире массовый автомобиль с двигателем V8
1967 Ford Fairlane — одна из наиболее удачных моделей Ford 1960-х годов.
Ford GT40 — легендарный гоночный автомобиль.
Ford Focus 2 ST
Компания выпускает широкий спектр легковых и коммерческих автомобилей под марками «Форд», «Линкольн», «Меркури». Под контролем Ford находятся такие известные производители автомобилей как Volvo Cars и Mazda.
Предприятия Ford расположены в США, РФ, Канаде, Мексике, Германии, Бразилии, Аргентине, Испании, Китае и прочих странах.
В состав Ford Motor Company входит крупное подразделение Ford of Europe со штаб-квартирой в Кёльне (Германия). Объём продаж Ford of Europe за 2007 год — 1,46 млн легковых и 369 985 коммерческих автомобилей. Президент Ford of Europe — Джон Флеминг.[10]
Модельный ряд
- Ford Explorer
- Ford Explorer I (1991—1994)
- Ford Explorer II (с 2003)
- Ford Explorer (U) (с 2002)
- Ford Explorer (U2) (1993—2003)
Концепт кары
- Ford Shelby Cobra Concept
Показатели деятельности
Общее количество занятых в компании — 280 тыс. человек (2006)[11].
Ford — третий по объёму выпуска автопроизводитель в мире после General Motors и Toyota. В 2006 году компанией (вместе с контролируемыми марками) было произведено 6,6 млн машин.
Выручка компании в 2007 году составила $173,9 млрд (в 2006 году — $160,1 млрд, в 2005 году — $178,1 млрд), чистый убыток — $2,7 млрд (в 2006 году — $12,6 млрд, в 2005 году — $1,6 млрд)[1][9].
Ford в России
История работы Ford в России
Компания открыла своё представительство и начала реализацию автомобилей ещё в Российской империи в 1907 году и продолжала свою деятельность после революции 1917 года.
Современное положение
В настоящее время на рынке России представлен в основном легковой модельный ряд европейского (немецкого) филиала Ford Werke GmbH., не имеющий прямого отношения к автомобилям американской Ford Motor Company.
Именно таковы модели «Fiesta» (импорт в США только планируется с 2011 года), «Fusion» (в США под этим названием продаётся седан класса «Мондео», европейская же модель не представлена), «Focus» (в США под таким именем продаётся фейслифтинг первого поколения европейского «Focus», на остальных рынках давно уже не продающегося), «Mondeo» (в США не представлен), «Kuga» (в США не представлен), «C-MAX» (представлен на североамериканском рынке импортируемыми машинами европейской сборки) и «S-MAX» (на рынке США не представлен). Эти модели разработаны силами европейского филиала «Форда» с расчётом на рынок Европы (точно так же, например, большинство автомобилей, продаваемых в Европе под американского происхождения брендом Chevrolet, на деле разработаны и выпускаются южнокорейским производителем Daewoo, ныне входящим в состав корпорации GM, и иным образом не связаны с автомобилями Chevrolet американского производства).
Из моделей же американского рынка в России представлены только внедорожники Ford Escape и Ford Explorer, имеющие огромные отличия от автомобилей немецкого филиала по внешнему и внутреннему дизайну, а также используемым компонентам. Иные модели североамериканской Ford Motor Company по состоянию на начало 2010 года в России официально не представлены.
В течение 2007 года в России было продано 175 793 автомобиля марки «Форд», из них 90 383 машины пришлось на Focus (являющийся самой продаваемой моделью автомобиля в стране). Очередь на поставку Focus составляет в среднем четыре месяца.[12]
Российское производство Ford
Российской дочерней компании Ford (ЗАО «Форд Мотор Компани») принадлежит автомобильный завод в городе Всеволожск (Ленинградская область), осуществляющий сборку автомобилей «Ford Focus 2» и Ford Mondeo (на предприятии производятся такие операции как сварка кузовов, окраска и окончательная сборка автомобилей). Предприятие было запущено в июле 2002 года и стало одним из первых автосборочных предприятий зарубежной марки в России.
Мощность завода на июль 2007 года составляла 72 тыс. автомобилей в год, численность персонала — 2,2 тыс. человек. Тогда же компания объявила о расширении мощностей всеволожского завода до 125 тыс. машин в год, в том числе 100 тыс. «Focus 2» и 25 тыс. «Mondeo». Инвестиции в расширение должны были составить $100 млн[13].
Российский завод Ford неоднократно становился ареной конфликтов между работниками и руководством, нередко выливавшихся в забастовки.
Спорт
Компания Форд принимает активное участие в спортивных соревнованиях по всему миру. Компания имеет собственную раллийную команду и активно поставляла двигатели для других команд.
Ралли
Формула-Форд
Формула-1
Компания Форд тесно связана с гонками Формула-1. Так, компания была одним из поставщиков двигателей для гоночных автомобилей этой серии (под маркой Cosworth) на протяжении сорока лет, а в 2000-м году купила команду Stewart Grand Prix, переименовав её в Ягуар. В 2004-м году команда была продана концерну Red Bull, а фирма Cosworth — Геральду Форсайту и Кевину Калкховену.
Критика
Американская ассоциация семьи, а также ряд других[14] общественных организаций приводили факты финансирования компанией Ford ряда мероприятий сексуальных меньшинств и телепрограмм гомосексуальной направленности[15] и, в связи с этим, призывали бойкотировать продукцию данного автопроизводителя. [16]
См. также
- Автобусы Ford
- Фордзон-Путиловец
- Большая детройтская тройка
Примечания
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Финансовые результаты Ford за 2007 год (предварительно) (ссылка проверена 09.03.07)
- ↑ Fortune 1000 (англ. яз.)
- ↑ Fortune Global 500
- ↑ Автомобиль-солдат
- ↑ Исаак Трабский. Генри Форд и Гитлер
- ↑ В США вышла книга о связях Генри Форда с нацистами
- ↑ Ford Motor получил прибыль. На Jaguar и Land Rover появились новые претенденты // Ведомости, № 138 (1912), 27 июля 2007
- ↑ Сергей Самсонов. Китайский Форд купил Volvo у американского // autonews.ru (Проверено 14 апреля 2010)
- ↑ 1 2 Глеб Столяров. «Места хватит для всех», — Найджел Брэкенбери, управляющий директор и президент Ford в России // Ведомости, № 35 (2057), 27 февраля 2008
- ↑ Александр Губский. «Страха перед профсоюзами нет», — Джон Флеминг, президент Ford of Europe // Ведомости, № 82 (2104), 7 мая 2008
- ↑ Годовой отчёт Ford Motor Company за 2006 год
- ↑ Глеб Столяров, Анатолий Темкин. Фокус с лицом // Ведомости, № 11 (2033), 23 января 2008
- ↑ Ford выбрал Mondeo. Всеволожский завод начнёт производить эту модель в 2008 г. // Ведомости, № 126 (1900), 11 июля 2007
- ↑ The public letter of 44 pro-family groups (англ. яз.)
- ↑ Top Ten Pro-Homosexual Sponsors on Television (англ. яз.)
- ↑ A project of American Family Association (англ. яз.)
Ссылки
- Официальный сайт компании (рус.)
- Глобальный официальный сайт компании(англ.)