Check VAT registration number for all EU countries, Norway, Switzerland and Thailand
Validate VAT number, calculate VAT at VAT rates of your EU client’s country, with currency converter
Free VAT number check, no registration needed
How to validate a VAT registration number?
Enter VAT registration number with country code included, and if you don’t know the country code, you can select it from the list. You can keep dashes, commas, spaces etc., they will be automatically cleaned. Along with EU and Northern Ireland VAT number, you can also check Swiss, Thai and Norwegian VAT registration number.
VATapp.net’s VAT number checker will then validate the VAT number. VAT number validation is performed against national tax administration databases: the EC VIES, Swiss UID register, Thai and Norwegian business register services. Using their service and contacting directly national tax administration are the only possible ways to validate a VAT number.
Validations quota (available/max):
Time until quota reset: ..h:..m:..s
VAT number result… Loading
Country:
| Country code:
Company name:
Company Address:
VIES consultation number:
Requester VAT number:
Source: The European Commission VIES-on-the-web
Disclaimer: VATapp.net shall not have any liability concerning the validation result.
Please consult VIES FAQ and VIES disclaimer for any questions.
VAT name
VAT rates & VAT calculator
VAT rate name
Present currency:
Calculate sales VAT from net or gross amount:
=
+ Add VAT (net price) — Subtract VAT (gross price)
Reduced rates for goods and services (Annex III ):
Loading map… Please wait…
How to check a non-EU VAT number?
VATapp.net checks VAT numbers only with those tax administrations that allow free and open access to its database in a machine-readable way (or the so-called API), for other way of getting confirmation of VAT number validity is usually not allowed, even if they do allow online VAT number validation. Most tax administrations don’t have open access via the API, but do provide online validation, namely, a page on their website where you can verify VAT number, however, mostly a single VAT registration number at a time.
Here is a list of some of them:
What VAT number validation results can you get?
VAT number validation process can have some of the next messages:
- VALID: success; VAT number is valid
- NOT VALID: success; VAT number is not valid
- VAT number format is not valid or country is not supported: error; the input VAT number does not have a valid format, it does not have correct country code, has extra number or other general error. VATapp.net’s VAT number validation service will automatically clean any strayed characters like spaces, commas, dashes etc. If you’ve recieved this message, you should check input data.
- The application at the Member State is not replying or not available.: error; VAT number validation service cannot get a response from EC VIES service. This usually means that EC VIES is overloaded with requests, so you should wait and try validating VAT number later.
Please note that Germany and Spain national tax administration databases do not provide address information. Some countries provide what seems to be postal address, instead of residential address.
Note: although a valid VAT ID number also indicates that a company exists, please note that VAT ID is usually not used to check existence of a company, only its current VAT registration status with tax administration database. A VAT ID number that is not valid doesn’t (always) mean the company doesn’t exist, but that it’s not registered for VAT at the given moment.
Does VATapp.net provide proof of VAT number validation?
No. VATapp.net does not provide any proof of validation. Validation is provided for informational purposes only, in accordance with terms and conditions of usage of the third party web services, and VATapp.net shall not have any liability concerning the validation results.
What is a VAT number?
VAT number (also called VAT identification number, VAT registration number, VAT ID, Tax identification number (TIN)) is an individual number of a registered business (so-called taxable person, as distinct from an individual person), that carries out taxable business transactions, and is obliged to register for VAT purposes.
How to get a VAT number?
VAT number can be issued only by a national tax administration. Taxable person that operates in the EU must register for VAT number in each EU member state, where it falls under the VAT Directive.
How to find a VAT number?
In some countries VAT number is publicly available, usually via official business register, so you can look it up by company name. Also, in some countries, it’s the same as the company registration number, which is prefixed with country code. If you have an invoice, it should be listed there. The recommended way is to ask your customer, in written form, so that you have a proof of communicating the VAT number.
How to batch check VAT number?
Paste in multiple VAT numbers in the form on VATapp.net’s batch VAT number check service. Your VAT numbers can have commas, dots, hyphens and other characters, VATapp.net will clean those. You can also batch check VAT number list that is separated by commas, tabs or spaces. You can get results as Excel, PDF or copy them. EU, Norway and Switzerland VAT number batch check is supported.
Where do VAT number validation results come from?
EU and Norther Ireland VAT number validation results are obtained from the VIES service, while Switzerland, Thailand and Norway VAT number validation results are obtained from respective national tax administrations’ databases. All VAT number check results are obtained in real time.
What is VIES?
VIES stands for VAT Information Exchange System on-the-web, it is created by the EC (European Commission) in accordance to combating fraud in the field of VAT Regulation and VAT Directive . VIES provides taxable persons performing intra-Community supply activities confirmation of validity of a VAT number by electronic means, while Member States are obliged to provide VAT number related data and keep that data up-to-date.
How to check Northern Ireland (UK) VAT number?
You can check Northern Ireland VAT number by entering VAT number in the following format: XI and number that can have 3-9 digits. Northern Ireland VAT number validation results are also obtained in real time from the EC VIES service.
How to check Norwegian VAT number?
Enter Norwegian VAT number in the following format: NO and number that can have 9 digits MVA. MVA part is optional. Norwegian VAT number validation results are obtained in real time from The Central Coordinating Register for Legal Entities (Enhetsregisteret) , Norway.
How to check Swiss VAT number?
Enter Swiss VAT number in the following format: CHE and number that can have 9 digits MWST/TVA/IVA. MWST/TVA/IVA part is optional. Swiss VAT number validation results are obtained in real time from UID register, The Swiss Federal Statistical Office (FSO) , Switzerland.
How to check if Thai tax ID is registered for VAT?
You can verify if Thai tax ID number is valid and registered for VAT, and by that, also check if the company exists and is registered in Thailand. Validation results include company’s name and address, if provided. You need company’s tax identification number (TIN), which is also used to check VAT registration status. Enter Thai TIN in the following format: TH and number that can have 13 digits. Please note that prefix TH is added for convenience. Thai VAT number validation results are obtained in real time from The Revenue Department (Thai: กรมสรรพากร), Thailand.
What is a VAT group?
VAT Group is usually a type of VAT regime or treatment, where a group of at least two companies register for VAT purposes as a single taxable person, i.e. VAT group (e.g. they submit VAT return for all members at once).
Usually, one company (holding company) controls others (subsidiaries). VAT group registration usually must be approved by national tax authority, which issues a single VAT number for all companies in the group as a whole.
In general, all members of the VAT group (VAT group entities) then use the VAT group VAT number, instead of their own (e.g. when issuing invoice). However, rules about VAT groups vary, they are not allowed in some countries, so you should check them with respective tax authority.
Why is VAT number important?
Among others, VAT number has a key role in:
The zero VAT rate for intra-Community supplies Supplier must obtain customer’s VAT number and have proof of communicating the VAT number. If the VAT number is valid, the zero VAT rate can be applied.
Issue of invoices When issuing invoices, VAT identification number is a mandatory information, so it must be contained on in invoice when doing business with EU clients.
VAT return and recapitulative statements VAT number is a mandatory information when submitting VAT return, as well as when submitting recapitulative statement.
While it looks very complicated, it is meant to simplify doing business, and of course, ensure tax collection.
These rules are regulated by EU legislation; you can read more about VAT and VAT number in VAT Directive and VAT invoicing rules
References:
‘VAT identification number’ means the number provided for in Articles 214, 215 and 216 of Directive 2006/112/EC;
Suppliers of electronic services, such as anti-virus updates are obliged to charge VAT on the service. If the purchaser of these services is a taxable person, then in certain circumstances, it is the customer, rather than the supplier who must account for the VAT. For this reason, the supplier may ask for the VAT identification number of the customer, so that he can confirm whether it is he who must charge the VAT or whether the customer himself will account for the VAT. If the customer does not have a valid VAT number, then the supplier will charge VAT.
It is necessary to ensure that the person you are supplying to in another Member State is a taxable person as this is one of the elements that define the correct VAT treatment. All taxable persons have the obligation to inform their tax administration that they perform VAT taxable transactions; in exchange, tax administration provides them with a unique VAT number. VIES on-the-web allows to validate whether the VAT number provided by your customer is registered in the relevant national database. The valid VAT number of your customer should be mentioned on your invoice
VAT numbers by country
Here is a list of EU and non-EU countries for which you can validate VAT numbers. The list contains information about each country’s VAT number: country code, VAT number format, description and example, as well as its local name and abbreviation.
Non-EU countries VAT number:
List of non-EU countries that have similar rules regarding the VAT number, which are regulated by organizations such as EEA or EFTA
| Country code/prefix: | NO |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Norwegian: | Organisasjonsnummer (Organization number) |
| Abbreviation: | Orgnr |
| VAT number format: | «NO»+9 digits and the letters «MVA», which indicates VAT registration, e.g. NO123456789 MVA. Additionaly, VATapp.net will show VAT register (Merverdiavgiftsregisteret) status and Enterprise Register (Foretaksregisteret) status. |
| Norway tax authority: | The Norwegian Tax Administration |
| Country code/prefix: | CH |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Swiss: | Mehrwertsteuernummer |
| Abbreviation: | MWST/TVA/IVA |
| VAT number format: | «CHE»+9 digits and the letters «TVA/MWST/IVA», which indicates VAT registration, e.g. CHE123456789 MWST. Additionaly, VATapp.net will show Commercial register status and VAT register status . |
| Switzerland tax authority: | Federal Tax Administration FTA |
| Country code/prefix: | XI |
|---|---|
| VAT number in English: | Value added tax registration number |
| Abbreviation: | VAT Reg No |
| VAT number format: | «XI»+ block of 9, 12 or 3 characters, e.g. XI123456789 |
| UK tax authority: | HM Revenue & Customs |
| Country code/prefix: | TH |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Thai: | เลขประจำตัวผู้เสียภาษีอากร |
| Abbreviation: | TIN |
| VAT number format: | block of 13 characters, e.g. 1234567890123 (TH is added for convenience) |
| Thailand tax authority: | The Revenue Department (Thai: กรมสรรพากร), Thailand |
EU countries:
Here is a list of VAT numbers of EU member states:
| Country code/prefix: | BE |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Dutch: | le numéro d’identification à la taxe sur la valeur ajoutée / BTW – identificatienummer |
| Abbreviation: | n° TVA, BTW-nr, Mwst-n |
| VAT number format: | «BE»+ block of 10 characters, e.g. BE123456789 |
| Belgium tax authority: | Service Public Fédéral Finances (Ministry of Finance, Belgium) |
| Country code/prefix: | CY |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Greek: | Αριθμός Εγγραφής Φ.Π.Α. / Arithmos Egrafis FPA |
| Abbreviation: | ΦΠΑ |
| VAT number format: | «CY»+ block of 9 characters, e.g. CY12345678L |
| Cyprus tax authority: | Ministry of Finance Tax Department |
| Country code/prefix: | CZ |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Czech: | daňové identifikační číslo (DIČ) |
| Abbreviation: | DIČ |
| VAT number format: | «CZ»+ block of 8 or 10 digits, e.g. CZ1234567890 |
| Czech Republic tax authority: | Finační správa (Financial administration) |
| Country code/prefix: | EE |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Estonian: | käibemaksukohustuslasena registreerimise number |
| Abbreviation: | KMKR |
| VAT number format: | «EE»+ block of 9 digits, e.g. EE123456789 |
| Estonia tax authority: | Maksu- ja Tolliamet (Tax and Customs Board) |
| Country code/prefix: | FI |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Finnish: | arvonlisãverorekisterõintinumero / Mervärdesskatteregistreringsnummer (momsregistreringsnummer) |
| Abbreviation: | ALV nro, Momsnummer |
| VAT number format: | «FI»+ block of 8 digits, e.g. FI12345678 |
| Finland tax authority: | Henkilöverotuksen viestintä (Finnish Tax Administration) |
| Country code/prefix: | PL |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Polish: | Numer identyfikacyjny VAT |
| Abbreviation: | NIP |
| VAT number format: | «PL»+ block of 10 digits, e.g. PL1234567890 |
| Poland tax authority: | Ministerstwo Finansów (Ministry of Finance) |
| Country code/prefix: | PT |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Portuguese: | o número de identificação para efeitos do imposto sobre o valor acrescentado |
| Abbreviation: | NIF or NIPC |
| VAT number format: | «PT»+ block of 9 digits, e.g. PT123456789 |
| Portugal tax authority: | Autoridade Tributária e Aduaneira (Tax and Customs Authority) |
| Country code/prefix: | ES |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Spanish: | el número de identificación a efectos del Impuesto sobre el Valor Añadido |
| Abbreviation: | NIF (CIF) |
| VAT number format: | «ES»+ block of 9 characters, e.g. ESX1234567R |
| Spain tax authority: | AGENCIA TRIBUTARIA (Tax Agency) |
| Country code/prefix: | SE |
|---|---|
| VAT number in Swedish: | Mervärdesskatteregistreringsnummer (momsregistreringsnummer) |
| Abbreviation: | Momsnr. |
| VAT number format: | «SE»+ block of 12 digits, e.g. SE123456789001 |
| Sweden tax authority: | Swedish Tax Agency |
Download Article
Download Article
If you run a business in a country that uses value-added tax (VAT), then VAT numbers from manufacturers are an important part of your paperwork. While a regular consumer doesn’t need to worry about VAT, you may need a company’s VAT number to track payments and tax collection for products you sell. You’ll also use VAT numbers to file tax returns to the government. Even if you’re new to the value-added tax system, VAT numbers are easy to find once you know where to look. Keep reading for everything you need to know about VAT numbers, including how to locate and validate them.
Things You Should Know
- Look at the company’s invoices, insurance forms, or tax documents for the VAT number. It will contain 2 letters and multiple digits.
- Try searching for the company on a VAT search engine to find their identification number.
- Contact the company directly and ask for their VAT number. You may need to submit a formal request to access the number.
- Validate the VAT number with an online VAT validation tool, or by calling the country’s business or tax department.
-
A VAT number is a tax ID code containing 2 letters and multiple digits. The VAT country code at the beginning of the ID is always 2 letters, and corresponds with the letters in a country’s name. The number of digits that come after the letters vary between countries, but they’re usually 8–12 numbers or letters. Each company has a unique VAT number, so no two will be the same.[1]
- Example: VAT numbers for Germany start with the letters “DE” and are followed by 9 digits, such as DE123456789.
- Example: The VAT country code for Estonia is EE, so an Estonian business’s VAT number may look like EE93810511
- The letters at the start of a VAT number may change based on the language you’re using. For example, the French VAT code is FR in English, but TVA in French. Use the right VAT code based on the government document that is requesting the information.[2]
- VAT is a type of tax that is charged incrementally by manufacturers based on the product’s value. The government uses VAT numbers to calculate charges and taxes across borders, as well as to determine prices for goods and services in the country where they’re being sold.[3]
Advertisement
-
1
Look at an invoice or insurance document to find a VAT number. If a company uses VAT taxes in their prices, they’ll usually list the company’s VAT number somewhere on the document. Check for VAT numbers near the letterhead on top of the page or by the information at the bottom.
-
2
Look for the company on a VAT search engine. If you know the company’s full name and the location where they’re based, you may be able to do a reverse lookup for their VAT number. Enter the country code for the country where the business is registered. Then, enter the company’s official name into the search bar to see if the VAT numbers are publicly listed.
- Most VAT number search engines are for companies based in the European Union (EU), but they may also show results for a few non-EU countries. If the company you’re inquiring about isn’t in the EU or UK, search the country’s name and the term “VAT registry.”
- You usually have to enter the official name listed on the business’s registration. So if you search for “Microsoft” when you’re looking for “Microsoft Indonesia,” you may not see any results.
- A company’s official name may be slightly different from its main product. For example, Pepsi is actually the name of a product while PepsiCo, Inc is the company name.
- Sometimes the search engines retrieve an outdated or incorrect VAT number. Always cross-reference the VAT number to guarantee its authenticity.
-
3
Contact a company directly to get their VAT number. Look for the company’s contact information and reach out to their tax department. Ask them for the VAT number and let them know what you need it for. If they have their VAT number as public information, they’ll tell you what it is over the phone.[4]
- You may need to file an official request document to solicit a company’s VAT number if it’s not public information.
- Some companies have multiple headquarters for different countries. For example, Apple is located in the United States, but Apple Ireland is located in Ireland. For tax purposes, they’re considered 2 different companies.
Advertisement
-
1
Use an online VAT number validation tool. The online validation tool you use depends on the country where the company is based. Just type the company’s VAT number into the tool and submit it. The corresponding business will pop up, and you’ll be able to verify that the number belongs to the right company.[5]
- Use the VIES search engine to validate the VAT number for companies in the EU.
- For companies based in the United Kingdom, use the UK government site to see if the VAT number is valid and learn the name and address it’s registered to.
- Companies outside of the EU and UK may have their own validation sites. Try searching online for the name of the country plus “VAT number validation” to find their sites.
-
2
Call the British VAT hotline for help looking up a number in the UK. Her Majesty’s Revenue and Customs (HRMC) is a government agency that regulates and monitors international business in the United Kingdom. If you’re located in the UK, dial 0300-200-3701. If you’re trying to contact the hotline outside of the UK, then dial +44-2920-5011-261. Tell the representative the VAT number and they’ll let you know if it’s valid or registered to anyone. [6]
- The HMRC helpline is only available during the week from 8 am to 6 pm BST.
-
3
Contact a country’s customs agency or business bureau. Any country using VAT will have a list of registered companies and their identification numbers. Look up the name of the country plus “customs agency” or “business bureau” to find the official government site. Contact the government agencies either over the phone or by email to ask them about the VAT number you found for a company. They’ll be able to help you find the correct information.[7]
Advertisement
-
Companies selling to countries with VAT have ID numbers. If any goods or services cross the border into a country that uses VAT, then that business is required to register for a VAT number. That way, the government can determine the amount of taxes they need to charge.[8]
- A total of 170 countries and territories use VAT.[9]
- The U.S. doesn’t use VAT since companies charge sales tax at a state level.
- VAT isn’t charged for financial services, education, property, or charity events.
- A total of 170 countries and territories use VAT.[9]
Our Most Loved Articles & Quizzes
Add New Question
-
Question
What is the VAT number for the US?
This answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff Editor
Staff Answer
The United States doesn’t use value-added tax or VAT numbers since states add individual sales tax. A company only needs a VAT number if they sell anything to countries that use value-added tax.
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
-
Always double-check VAT numbers to ensure they’re correct and valid. If you submit any tax forms with the wrong VAT numbers, your business will have to pay the bill for the tax claim, and it can create issues with a business’s tax documentation.
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 243,638 times.
If you buy through links on our site, we may earn a commission.
Did this article help you?
Публикация
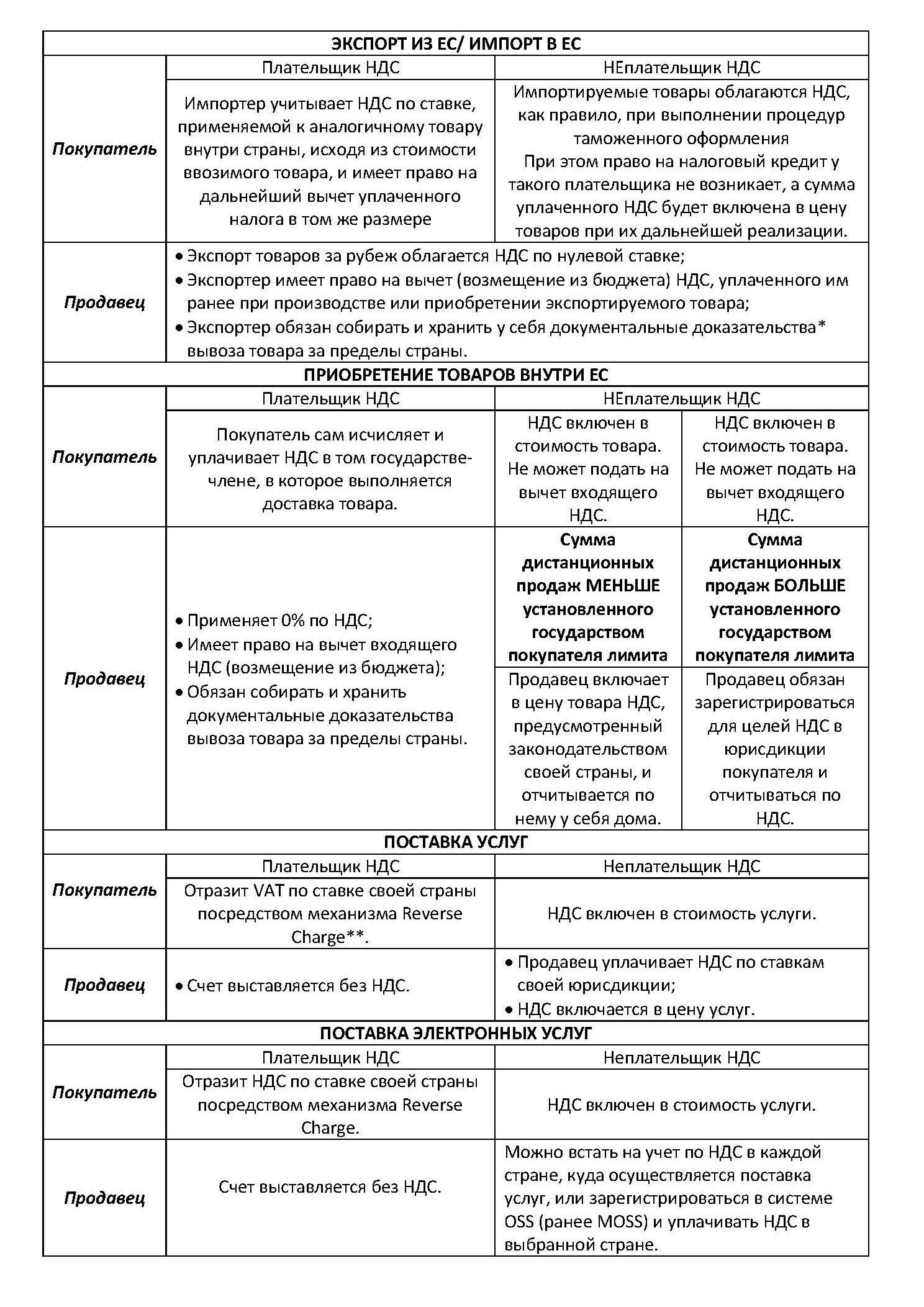
Вопросы европейского НДС, а также связанные с ним вопросы по получению VAT номера, очень часто возникают у предпринимателей, осуществляющих экспортно-импортные поставки товаров как внутри ЕС, так и за его пределы, а также при оказании услуг клиентам на территории ЕС.
Помимо классической реализации товаров через розничные точки, сегодня большую популярность набирают интернет-магазины: когда товары находятся на складе в одной стране, при этом после оформления заказа через сайт товар направляется непосредственно потребителю, который может находиться в любой другой стране ЕС или за его пределами.
Не меньшей популярностью сегодня могут похвастаться и интернет услуги: сайты знакомств, образовательные интернет-площадки, сайты, предоставляющие видео-, аудио- и фотоконтент, электронные площадки, на которых пользователи имеют возможность найти друг друга и согласовать условия по оказанию логистических услуг, поиску специалистов и многое другое.
При этом практически во всех перечисленных выше случаях будут возникать обязательства по расчету и уплате НДС, соответственно появится необходимость в получении VAT номера. Многие предприниматели сталкиваются с определенными сложностями при регистрации в качестве плательщика НДС (получении VAT номера), ведь, несмотря на гармонизированные правила НДС в ЕС, каждая отдельная страна имеет свои местные требования к регистрации по НДС и свои внутренние ставки.
Value Added Tax Identification Number (VAT или, как его еще иногда называют, VATIN) – это уникальный номер, который идентифицирует налогооблагаемое лицо (бизнес) или необлагаемое налогом юридическое лицо, зарегистрированное в качестве плательщика НДС.
Таким образом, VAT номер необходим в том случае, когда деятельность связана с начислением и уплатой НДС.
Следует напомнить, что НДС – это косвенный налог, налог на потребление. Он применяется к более или менее всем товарам и услугам, покупаемым или приобретаемым для использования или потребления.
Нет. Каждая страна ЕС выдает свой собственный национальный номер плательщика НДС.
VAT номера в странах ЕС различаются в зависимости от страны, в которой налогоплательщик регистрируется в качестве плательщика НДС. VAT номер обычно состоит из 2 букв, обозначающих государство, и кода, состоящего из 8 – 12 цифр.
Ниже приведены примеры VAT номеров по странам-членам ЕС.
Не стоит путать такие понятия как идентификационный номер (Tax Identification Code – TIC или Tax Identification Number – TIN) и VAT номер налогоплательщика.
TIN номер присваивается однократно при регистрации юридического лица. Это один из основных реквизитов, который используется в разных документах, таких как счета-фактуры, платежные поручения (налоги и страховые взносы), заявления и документы в налоговую инспекцию.
VAT номер, в свою очередь, необходим только в том случае, если юридическое лицо подпадает под требования регистрации для целей уплаты НДС.
Налоговый идентификационный номер (TIN) на Кипре состоит из 8 цифр и 1 буквы, в то время как VAT номер состоит из 2х букв 8 цифр и еще 1 буквы, что в целом несложно перепутать.
Кроме того, если налогоплательщик ведет внешнеэкономическую деятельность на территории ЕС, то он также столкнется с таким понятием как EORI номер, который необходим для прохождения таможни.
EORI – это уникальный номер (код) идентификации субъекта предпринимательской деятельности Европейского Союза в единой централизованной базе данных предприятий, которые ведут внешнеэкономическую деятельность на территории ЕС.
EORI номер представлен 2 буквами, обозначающими государство, 10 цифрами и снова 5 буквами. Например: UA1234567890ASDFG.
Иностранные компании, как из ЕС, так и не входящие в зону ЕС, могут работать в любой стране ЕС без необходимости формирования местных компаний и филиалов, зарегистрировавшись в качестве плательщика НДС.
Если юридическое лицо, осуществляющее хозяйственную деятельность в ЕС, поставляет товары или услуги другому юридическому или физическому лицу, то такое юридическое лицо в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств может/обязано зарегистрироваться в местных налоговых органах, взимать налог с покупателей и подавать отчетность по НДС.
Кроме того, страны ЕС самостоятельно устанавливают размер порогового значения и сроки, необходимые для регистрации в качестве плательщика НДС.
Отдельные пороговые значения могут быть предусмотрены для дистанционных продаж при приобретении товаров и услуг между странами ЕС.
Кипр – стоимость налогооблагаемых сделок за 30 дней составляет 15 600 евро или прибыль за последние 12 месяцев торговли составила не менее 15 600 евро.
Венгрия – порог отсутствует, за исключением дистанционной торговли, для которой он составляет 12 000 000 форинтов (примерно 48 000 евро).
Польша – годовой оборот не превышает эквивалента 40 000 евро в национальной валюте.
Юридические лица, предлагающие свои услуги через каналы электронной связи конечным потребителям на территории ЕС, не являющимися плательщиками НДС, обязаны выбрать юрисдикцию в составе ЕС, чтобы зарегистрироваться в ней в качестве плательщика НДС и отчитываться по нему.
До начала регистрации и получения VAT номера необходимо определиться, у кого и в какой юрисдикции будут возникать обязательства по уплате НДС.
Такие обязательства в первую очередь зависят от вида поставки – товар или услуга, а также от того, кто будет выступать получателем услуги – юридическое лицо (бизнес – бизнесу / B2B) или конечный потребитель (бизнес – конечному клиенту / B2C).
Согласно Директиве 2006/112/EC (далее – Директива) выделяются 4 типа налогооблагаемых операций для целей НДС (в каждом типе есть еще 2 подтипа: B2B и B2C).
По общему правилу при поставке товаров обязательства по уплате НДС возникают по месту поставки, но определение места поставки зависит от множества факторов и условий.
По общему правилу обязательства по уплате НДС будут возникать по месту поставки товара.
Представим, что компания, зарегистрированная в Венгрии, собирается приобрести товар у компании, зарегистрированной в Литве, и продавать данный товар в Италии. При этом склад, на который будет транспортироваться данный товар, будет находиться также в Италии (товар на территорию Венгрии заходить не будет). В этом случае венгерская компания должна будет встать на VAT учет в Италии, начислить его и отобразить в отчетности вычет на эту же сумму. Фактической уплаты VAT не происходит.
В данном случае необходимо сравнивать суммы сделок от продаж с порогами для целей регистрации по НДС в каждой юрисдикции. Если сумма сделок превышает установленный порог, то необходимо будет зарегистрироваться для целей уплаты НДС в местных налоговых органах.
Если пороги по сделкам для целей регистрации по НДС превышены в нескольких юрисдикциях, то зарегистрироваться по НДС придется во всех юрисдикциях, где такой порог превышен.
Импортируемые товары облагаются НДС, как правило, при выполнении процедур таможенного оформления в целях выпуска товара в свободное обращение. Импортер уплачивает НДС по ставке, применяемой к аналогичному товару внутри страны исходя из стоимости ввозимого товара, и имеет право на дальнейший вычет уплаченного НДС в том же размере.
По общему правилу, услуги B2B облагаются НДС по месту нахождения заказчика (получателя) услуг (Destination principle).
Если услуги оказаны неплательщику НДС, то услуга облагается по принципу происхождения (Origin principle), то есть местом поставки услуг будет считаться место регистрации бизнеса поставщика.
В случае, когда мы говорим про оказание услуг, также необходимо понимать, что услуги условно можно разделить на 2 вида – классические услуги (в нашем понимании), такие как консультационные, юридические, бухгалтерские, аудиторские, инжиниринговые, рекламные, маркетинговые услуги, услуги по обработке информации и т.д., и электронные услуги – поставка видео, музыки, игр, лотерей и других азартных игр, услуги веб-сайтов, программные услуги (предоставляемые через Интернет), поставка дистанционного обучения (автоматизированное дистанционное обучение), предоставление текстов, изображений и баз данных.
Таким образом, для того, чтобы определить, будут ли возникать обязательства по НДС в ЕС, необходимо провести краткий анализ своей деятельности по следующим аспектам:
- Будет ли деятельность носить экспортный / импортный характер или осуществляться внутри ЕС? Иными словами, где находятся продавец и покупатель – в ЕС или за его пределами?
- Ваш клиент – юридическое лицо (B2B) или конечный потребитель (B2C)? В случае работы с юридическим лицом необходимо запрашивать у Вашего контрагента VAT номер, так как юридический статус не указывает на то, что контрагент является плательщиком НДС в стране своей регистрации. Если контрагент не может предоставить VAT номер по какой-либо причине, то такая сделка будет рассматриваться как сделка с конечным потребителем.
- Речь идет о поставке товаров или оказании услуг?
- Какова юрисдикция покупателя? Особенно важно учитывать юрисдикции покупателей при работе с конечными потребителями, так как в этом случае обязанность по исчислению и уплате НДС возлагается на продавца.
- Сумма продаж превышает лимит, установленный страной покупателя для целей регистрации по НДС? Это необходимо в случае приобретения товаров / услуг внутри сообщества, а также при оказании электронных услуг.
Ниже представлена краткая сводная таблица по обязательствам по НДС в ЕС. В таблице приведены общие правила НДС в ЕС (правила значительно упрощены для наглядности и общего понимания, а также не учтены исключения). Каждый случай уникален и требует отдельного детального анализа.
Под неплательщиками НДС понимаются конечные потребители и юридические лица, незарегистрированные в качестве плательщиков НДС, или непредоставившие свой номер регистрации по НДС.
* Таможенные декларации, транспортные накладные и сопутствующая документация (деловая переписка, контракты, расписки и т.п.).
** Reverse Charge — это механизм учета НДС по операциям при поставке услуг, когда местом поставки таких услуг является страна получателя.
Для применения этого механизма между контрагентами должны быть соблюдены следующие условия:
- контрагенты должны быть из разных государств;
- место поставки услуг совпадает с местом регистрации получателя услуг в государстве, входящем в состав ЕС;
- получатель услуг должен быть плательщиком НДС.
При соблюдении этих условий поставщик услуг выставляет инвойс без НДС, а обязательство отчитаться по нему переходит к получателю услуг. Получатель на сумму услуги начисляет НДС по ставке своей страны и тут же указывает ее к налоговому вычету. Фактической уплаты налога не происходит, операция отражается исключительно в отчетности по НДС.
Упрощенная система регистрации по НДС применяется только при оказании электронных услуг.
Под электронными услугами понимаются услуги, поставляемые через Интернет или электронные сети, которые могут в основном предоставляться автоматически с минимальным вовлечением людей и предоставление которых невозможно без информационных технологий.
- услуга отличается от физической поставки товара;
- основана на информационных технологиях;
- предоставляется электронным способом, через Интернет, медный или оптоволоконный кабель, а также по радиоканалу или через спутники;
- поставка практически полностью автоматизирована.
Особенностью предоставления таких услуг является переход на принцип «по месту назначения», то есть местом поставки таких услуг считается место нахождения получателя услуг.
Для упрощения администрирования и отчетности по НДС поставщик электронных услуг может избежать необходимости постановки на налоговый учет в каждой из стран ЕС, где находятся клиенты компании, и выбрать использование системы MOSS.
Данная система позволяет компании зарегистрироваться для целей НДС по электронным услугам только в одной стране ЕС по своему выбору.
Налоговые органы этой страны самостоятельно информируют и переводят платежи в страны нахождения потребителей услуг на основе информации, указанной в декларации. Для этих целей в декларации указываются суммы продаж по каждой стране и рассчитывается НДС, исходя из ставки налога в каждой такой стране.
Законодательство ЕС устанавливает, что стандартная ставка НДС не может быть меньше 15%, а льготная меньше 5% (на строго определенные списки товаров и услуг). Сами ставки и списки товаров и услуг с льготными ставками устанавливаются каждой страной.
В настоящий момент самая низка ставка по НДС в ЕС равна 17% и применяется в Люксембурге, а самая высокая в Венгрии и составляет 27%. Со ставками по НДС в других странах членах ЕС можно ознакомиться в таблице ниже.
|
Страна |
Стандартная ставка по НДС |
|
Австрия |
20% |
|
Бельгия |
21% |
|
Болгария |
20% |
|
Кипр |
19% |
|
Чехия |
21% |
|
Германия |
19% |
|
Дания |
25% |
|
Эстония |
20% |
|
Испания |
21% |
|
Финляндия |
24% |
|
Франция |
20% |
|
Греция |
24% |
|
Хорватия |
25% |
|
Венгрия |
27% |
|
Ирландия |
23% |
|
Италия |
22% |
|
Литва |
21% |
|
Люксембург |
17% |
|
Латвия |
21% |
|
Мальта |
18% |
|
Нидерланды |
21% |
|
Польша |
23% |
|
Португалия |
23% |
|
Румыния |
19% |
|
Швеция |
25% |
|
Словения |
22% |
|
Словакия |
20% |
Запрашивать VAT номер необходимо для корректного исчисления и уплаты НДС. В случае, если контрагентом будет выступать лицо – плательщик НДС, но при этом продавец не сможет получить его VAT номер, все операции с данным контрагентом необходимо будет учитывать как операции с конечным потребителем – неплательщиком НДС.
В ЕС идентификационный номер VAT можно проверить на официальном сайте VIES (VAT Information Exchange System). Это общеевропейская система обмена информацией по действительности VAT номеров компаний, зарегистрированных в ЕС. Также через VIES передается информация о внутрисоюзных поставках, которые освобождаются от налогообложения.
В начале 2021 года Великобритания вышла из состава ЕС, в связи с чем гармонизированные правила и нормы ЕС больше не распространяются на Великобританию, в частности и правила в отношении НДС. Для целей НДС Великобритания в настоящее время рассматривается как любое иное третье государство, не входящее в ЕС.
В Великобритании лицо обязано зарегистрироваться для целей НДС в случае, если в любой 12 месячный период товарооборот превысит 85 000 фунтов (примерно 100 000 евро).
При оказании электронных услуг потребителям, которые находятся в Великобритании, с 1 января 2021 года больше нельзя воспользоваться системой OSS. Это значит, что в случае, если потребители электронных услуг будут находиться как на территории ЕС, так и в Великобритании, необходимо будет регистрироваться для целей НДС, как в ЕС, так и в Великобритании.
Поделиться в социальных сетях:
If your customer is a business like you, they’ll expect not to pay VAT and likely have a VAT number to prove it. All you need to do is verify if they are really a business before zero-rating VAT.
What is a VAT Number
The VAT number is a unique code which a business is given when it registers itself with a tax authority in the European Union.
As the supplier you must state your customer’s validated VAT number on the invoice. This means that you should re-validate VAT numbers whenever a scheduled charge becomes due (for example on a subscription model).
Some EU member state databases do not disclose the business’s name and address for privacy reasons, so you’ll have to trust that your customer is providing its own VAT number.
Why You Have to Validate EU VAT Numbers
Online businesses are unlike brick and mortar stores. If a physical product enters the EU, it is taxed at the customs. Digital products obviously don’t cross any borders that can pass through customs, so they have VAT added. Digital products are any Telecommunication, Broadcasting and Electronic (TBE) services, or collectively called electronically supplied services (ESS). We’ve written more information about such electronically supplied services.
If foreign businesses didn’t have to charge a VAT, imagine how disadvantaged EU-based businesses would become. Their products and services would cost more to the consumer.
Lawmakers have therefore decided that businesses themselves will be held accountable for charging the correct VAT to all their EU citizens. This is regardless whether your business is operating from within or from outside the EU.
Customers can pretend to be a business just to avoid taxes, and you will end up owing the VAT amount to tax administrations.
A customers who cannot provide a VAT number must be charged a VAT at the rate applicable at their location. It will no longer be possible to exempt VAT as of January 1, 2020 without a validated VAT number of your customer stated on the invoice. A customer’s valid VAT number is a substantive requirement for applying the zero VAT rate to intra-community supplies of goods.
Note that the chargeable event for digital products takes place at the customer’s location, not your business’s location. We’ve written about the VAT rules in the European Union for your reference. For example, if your customer is normally residing in Belgium, you would have to charge the Belgian VAT rate of 21% (reduced VAT rates may apply for certain types of digital products).
How to Validate the EU VAT Number of Your Customer
When you check a VAT number, your request goes to the database of the respective EU member state in real-time. This mechanism is made possible by the VAT Information Exchange System (VIES) of the European Commission. If the number appears invalid, you should either reject it or contact your customer to rectify the situation.
There are two ways to validate EU VAT numbers:
1. Manually
The status of a EU VAT number issued by any EU country can be manually checked via VIES. VIES checks the registration status of EU VAT numbers against the records maintained by the respective member state. Select the country code (member state) where your customer resides and enter the VAT number.
If you have a VAT number yourself, you can enter it in the fields underneath. This will additionally request a unique reference number which is a piece of evidence showing that you have validated a given VAT number on a given date.
Click the Verify button to obtain a response:
2. Automatically
In order to automate VAT number checks during your customer’s checkout process, you would implement an API. Most online businesses selling digital products have an automated process to validate their customer’s VAT number during checkout. This gives customers immediate feedback when they enter an invalid VAT number, and saves you manual work.
Our validations REST API lets you validate VAT numbers in real-time. Responses are returned to you in JSON format.
A JSON response for VAT number IE6388047V will look like this:
{
"id": "5d1ded3128ca7a842aaf5ed4",
"company_address": "3RD FLOOR, GORDON HOUSE, BARROW STREET, DUBLIN 4",
"company_name": "GOOGLE IRELAND LIMITED",
"company_type": null,
"consultation_number": "WAPIAAAAW21qsOHW",
"country_code": "IE",
"query": "IE6388047V",
"type": "eu_vat",
"valid": true,
"valid_format": true,
"vat_number": "6388047V",
"requested": "2019-07-04T00:00:00.000Z",
"created": "2019-07-04T12:12:33.322Z",
"updated": "2019-07-04T12:12:33.322Z"
}3. Automated Mass Validation
If you have to check a large number of VAT numbers at a time, you can use our dashboard to check VAT numbers in bulk.
Upload a CSV file and start the validation process. Once finished, you’ll be notified via email and can download the complete report containing VAT registration status and official company data.